The Benefits of a Private Blockchain
A private blockchain is a blockchain that is owned and controlled by a specific group or individual. This type of blockchain provides many benefits over public blockchains, including increased security and privacy.
One major benefit of private blockchains is that they are more secure. Because they are owned and controlled by a specific group or individual, private blockchains are immune to attacks from other parties. This makes them a much more reliable platform for conducting business transactions.
Private blockchains also provide greater privacy than public blockchains. Because they are not publicly accessible, private blockchains are less likely to be tampered with. This increases the security and privacy of all data stored on the platform.
Finally, private blockchains can be more efficient than public blockchains. Because they are owned and controlled by a specific group or individual, private blockchains are able to operate more quickly and efficiently than public blockchains. This makes them a more effective platform for conducting business transactions.
The Advantages of a Private Blockchain
There are many benefits to using a private blockchain, including:
decentralization – the network is not subject to the control of a single entity or organization
security – the data is not accessible by anyone other than those authorized to view it
transparency – all participants can see all the data and transactions on the network
efficiency – a private blockchain can be more efficient than a public blockchain because it eliminates the need for a third party to process transactions
integrity – the accuracy of data is maintained because it is not shared with other parties
consensus – a private blockchain requires the participation of all members of the network in order to make changes, or transactions will not be accepted
No Third Party is Necessary
One of the main advantages of a private blockchain is that it eliminates the need for a third party to process transactions. This is because the network is decentralized, meaning that there is no central authority that can approve or disapprove transactions. In a public blockchain, such as Bitcoin, transactions are processed by a network of nodes run by miners.
This process can be time-consuming and expensive, which is why many traditional businesses are now exploring the use of private blockchains. Because private blockchains are not open to the public, they are more secure than public blockchains. This is because it is difficult for outsiders to access and modify the data.
Efficient Transaction Processing
Another advantage of using a private blockchain is that it can be more efficient than a public blockchain. This is because a private blockchain does not require a third party to process transactions. Instead, the network itself executes these transactions.
This process is faster and more efficient because there is no need for a large number of nodes to be operational. In addition, a private blockchain does not require a consensus mechanism, which is a rule that all participants must agree on in order for a transaction to be processed. This is why private blockchains are often used for financial applications, such as asset management and trade settlements.
Security and Privacy
One of the main benefits of using a private blockchain is that it offers security and privacy. Because the network is decentralized, data is not accessible by anyone other than those authorized to view it. This means that data cannot be tampered with or stolen.
Additionally, because all participants can see all the data and transactions on the network, it is easier to verify the accuracy of data. This is especially important in financial applications, where there is a risk of fraud.
Governance and Consensus
One of the key advantages of using a private blockchain is that it requires the participation of all members of the network in order to make changes, or transactions will not be accepted. This is why private blockchains are often used for applications such as asset management and trade settlements.
Because all members need to agree on changes, consensus is required in order for the network to function. This makes private blockchains more reliable than public blockchains, which are susceptible to attacks that can disrupt or damage the network.
The Purpose of a Private Blockchain
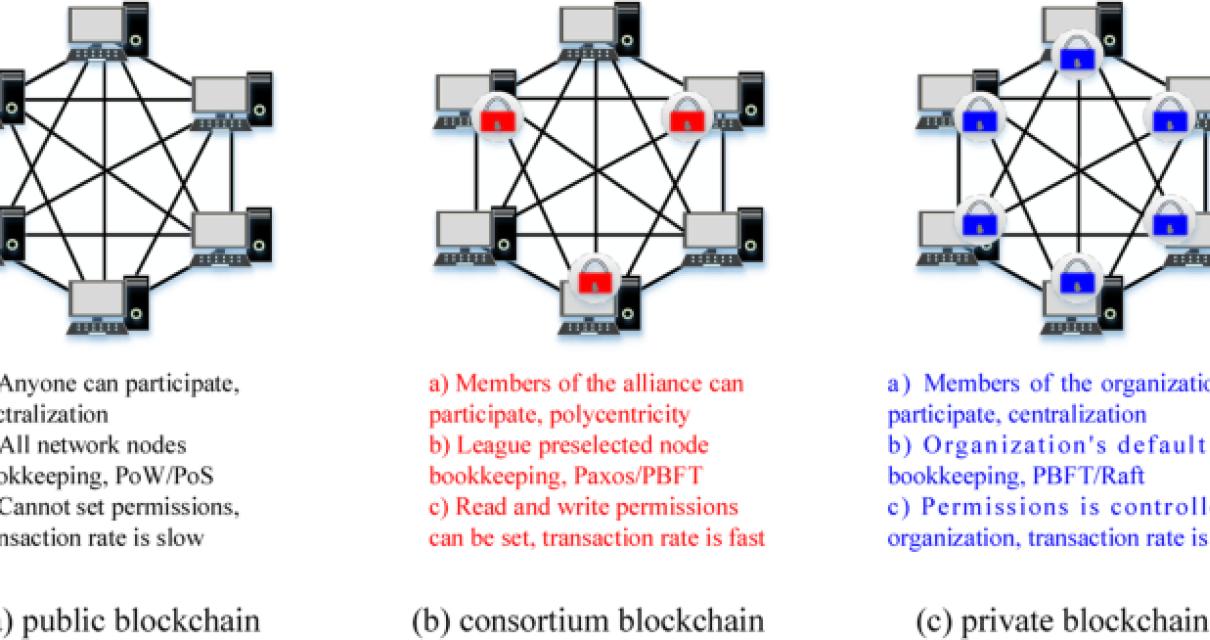
A private blockchain is a blockchain that is not open to the public. Private blockchains are typically used for business transactions and other confidential operations.
Private blockchains have several advantages over public blockchains. For example, a private blockchain can be more secure because it is not publicly accessible. Private blockchains also have the ability to track transactions more accurately because they are not subject to the same transparency constraints as public blockchains.
Private blockchains have also been used to create decentralized applications (dApps). A dApp is a piece of software that runs on a private blockchain. dApps can be used to create all sorts of new applications.
The Usefulness of a Private Blockchain
A private blockchain is a type of blockchain network that is operated by a single entity or group of entities. This type of blockchain network can be more secure and efficient than a public blockchain network, which is why it is becoming more popular.
A private blockchain can be used to create a more efficient and secure network for businesses. It can also be used to track the ownership and distribution of assets. In addition, private blockchains can be used to create a decentralized platform for applications.
The potential uses for a private blockchain are endless, and the technology is still relatively new so there are still many opportunities to explore.
Why Have a Private Blockchain?
A private blockchain is a blockchain that is not publicly available. Private blockchains are used for a variety of reasons, including:
Private blockchains are used to create a tamper-evident record of transactions.
Private blockchains are used to create a secure network.
Private blockchains are used to create a decentralized system.
What is the Point of a Private Blockchain?
The point of a private blockchain is to create an isolated, secure network for a specific group of people or organizations. This can be used for a variety of purposes, such as tracking shipments or issuing bonds.
How Does a Private Blockchain Benefit Me?
A private blockchain can benefit you in a few ways. First, it can provide a secure, tamper-proof record of transactions. This can be especially helpful in industries where transactions are sensitive or regulated, such as finance or healthcare. In addition, a private blockchain can help reduce the cost and time required to conduct transactions. Finally, a private blockchain can provide a platform for developing new applications.