How Smart Contracts Work in Blockchain
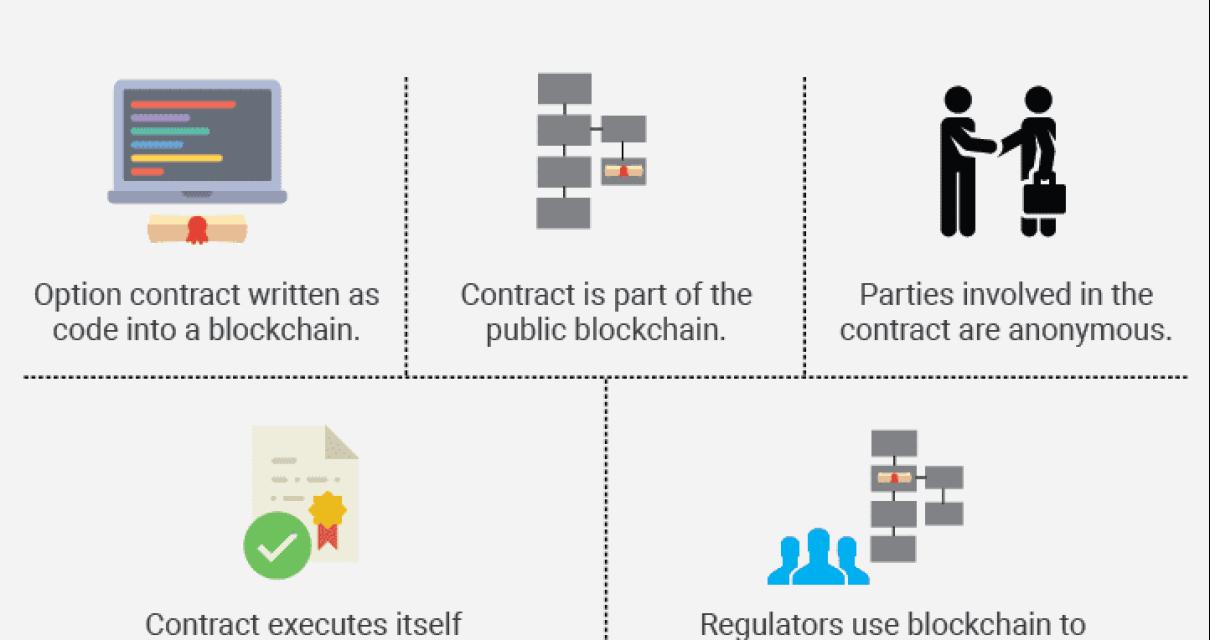
A smart contract is computer code that operates as a self-executing contract. When two or more parties agree to the terms of a contract, they create a smart contract. This code is stored on a blockchain, which is a digital ledger of all cryptocurrency transactions.
When someone wants to buy something from a seller, they send the seller cryptocurrency. The seller then broadcasts a message to the entire blockchain network that says they’ve agreed to sell this item for this amount of cryptocurrency. Any interested buyers who have the cryptocurrency can then validate the transaction by sending the seller their coins. Once the seller receives the coins, they can use them to purchase the item.
Since there’s no central authority overseeing smart contracts, they’re theoretically immune to fraud and censorship. This makes them ideal for use in a variety of applications, includingproperty transactions, financial settlements, and crowdfunding.
The Benefits of Smart Contracts in Blockchain
Smart contracts can provide a number of benefits in the world of blockchain. These include:
1. Increased Security and Transparency: Smart contracts are designed to increase security and transparency by ensuring that all actions taken within them are enforced. This means that both parties involved in a contract can be sure that the terms of the agreement will be followed.
2. Reduced Costs and Time: Smart contracts can reduce costs and time by automating the process of completing a contract. This can save both parties time and money, as well as reducing the chances of any disputes arising.
3. Reduced Risk: Smart contracts are designed to reduce risk by ensuring that all parties involved are fully aware of the terms and conditions of the contract. This means that there is no chance of disputes arising, which can lead to costly legal proceedings.
4. Improved Efficiency: Smart contracts can improve efficiency by automating the process of completing contracts. This can save both parties time and money, as well as reducing the chances of any disputes arising.
5. Increased Trust: Smart contracts are designed to increase trust by ensuring that all actions taken within them are verified and recorded. This means that both parties involved in a contract can be sure that the terms of the agreement will be followed.
The Risks of Smart Contracts in Blockchain
There are a few risks associated with smart contracts in blockchain.
The first risk is that a smart contract may not be properly coded, which could lead to errors or vulnerabilities. If a smart contract is not properly coded, it could be attacked and exploited, resulting in loss of funds or other damages.
Another risk is that a smart contract may not be executed as intended. If the code for a smart contract is not properly executed, it could result in a failure of the contract, which could lead to financial losses for the parties involved.
Lastly, a smart contract may be hacked. If someone gains access to a smart contract and exploits any vulnerabilities, they could potentially steal funds or other assets from the participants involved in the contract.
What is a Smart Contract?
A Smart Contract is a digital contract between two or more parties that is executed and enforced through the use of blockchain technology. Smart Contracts allow for the automatic execution of a transaction between parties, without the need for a third party.
How Do Smart Contracts Work?
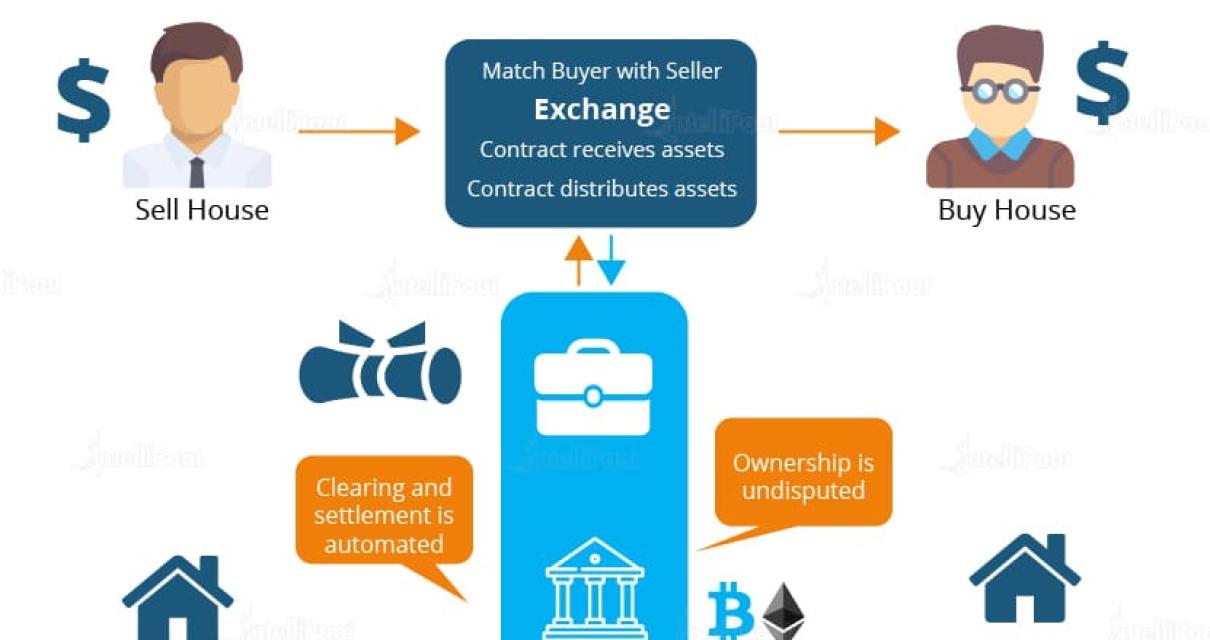
A smart contract is a computer protocol designed to facilitate, verify, or enforce the negotiation or performance of a contract. It operates on a blockchain, a distributed database that can be used to record transactions. The blockchain uses a distributed consensus mechanism to ensure that all transactions are recorded and processed by the network.
A smart contract contains code that allows two or more parties to exchange information and to execute a transaction. When a party initiates a transaction, the code in the smart contract activates and performs the agreed-upon actions. Smart contracts are autonomous and self-executing. This means that they automatically carry out the terms of the agreement between the parties.
Smart contracts can be used to create a variety of digital contracts, including property, securities, and contract-based crowdfunding. They can also be used to automate governance and financial processes.
What are the Benefits of Smart Contracts?
There are many benefits to using smart contracts, including:
1. Automated Transactions: Smart contracts allow for automated transactions, which can reduce the need for human interaction and potentially increase efficiency.
2. Security and Transparency: Smart contracts are secure and transparent, meaning that all information is available for inspection before and after a transaction takes place. This ensures that both parties know what they are signing up for.
3. tamper-proofed: Smart contracts are tamper-proofed, meaning that they are impossible to change or hack without being noticed. This enhances trust and security between parties involved in a transaction.
4. Reduced Risk: By using smart contracts, businesses can reduce their risk of fraud and other potential problems. This can lead to increased efficiency and decreased costs.
What are the Risks of Smart Contracts?
The risks of smart contracts include the potential for a hacker to gain access to a contract’s code and alter it, leading to a loss for the party that made the contract. Additionally, there is the potential for a contract to be invalidated due to a technical flaw. If this happens, the party that made the contract may not be able to receive the agreed-upon benefits.
How Can I Use Smart Contracts?
Smart contracts are a way to make a contract between two or more parties where the terms of the contract are automatically enforced by code. The code is stored on a blockchain, making it tamper-proof and transparent. This makes Smart Contracts an ideal way to create trustless contracts, where both parties have confidence that the terms of the contract will be upheld.
One use of Smart Contracts is to create a tamper-proof system for escrow or other financial transactions. For example, a company may want to use Smart Contracts to manage the transfer of money between two parties in a trade. The code will automatically verify that the transaction is complete and release the funds to the appropriate party once the conditions of the contract have been met.
Smart Contracts can also be used to automate complex legal contracts. For example, a company may want to use Smart Contracts to create a contract between itself and a supplier. The contract could include details such as the amount of goods that the supplier is expected to provide, the delivery date, and the payment terms. The contract would be automatically executed once all the necessary details had been agreed upon.
Finally, Smart Contracts can be used to enforce conditions in other contracts. For example, if you are contracting to deliver flowers on a certain day, you could use a Smart Contract to ensure that the flowers are delivered on time. The code would automatically contact the florist when the delivery was due and check to see if the flowers had been delivered. If not, the contract would trigger an event that would cause the flowers to be delivered on time.
What is the Future of Smart Contracts?
The future of smart contracts is bright. As the technology evolves and becomes more user-friendly, there is potential for smart contracts to become increasingly popular and widely used. Some possible applications of smart contracts include:
-The use of smart contracts to automate the management of securities and other financial assets
-The use of smart contracts to automate the management of supply chains
-The use of smart contracts to automate the management of customer relationships
-The use of smart contracts to automate the management of physical assets
Which Blockchains Support Smart Contracts?
Bitcoin and Ethereum are the first blockchains that support smart contracts. Other blockchains that support smart contracts include Ripple, EOS, and NEO.