What is a smart contract blockchain?
A smart contract blockchain is a distributed ledger system that allows for the execution of contracts between two or more parties. Smart contracts are self-executing, meaning that once a set of conditions are met, the contract will automatically execute its terms. This eliminates the need for a third party to mediate or enforce the contract’s terms.
How can a smart contract blockchain benefit businesses?
The biggest benefit of using a smart contract blockchain for businesses is that it allows them to avoid the need for a middleman. This is particularly important for businesses that operate in highly regulated industries, such as finance or healthcare. By using a smart contract blockchain, businesses can ensure that all transactions are recorded and verified instantly, without the need for a third party. This means that businesses can save on costs associated with traditional processing methods, such as fees and commissions.
What are the key features of a smart contract blockchain?
A smart contract blockchain is a distributed database that allows parties to create and manage contracts. Smart contracts are self-executing contracts that are verified and enforced by the network. This removes the need for a third party to mediate and ensure the contract is upheld. Smart contracts also allow for transparent and tamper-proof recordkeeping.
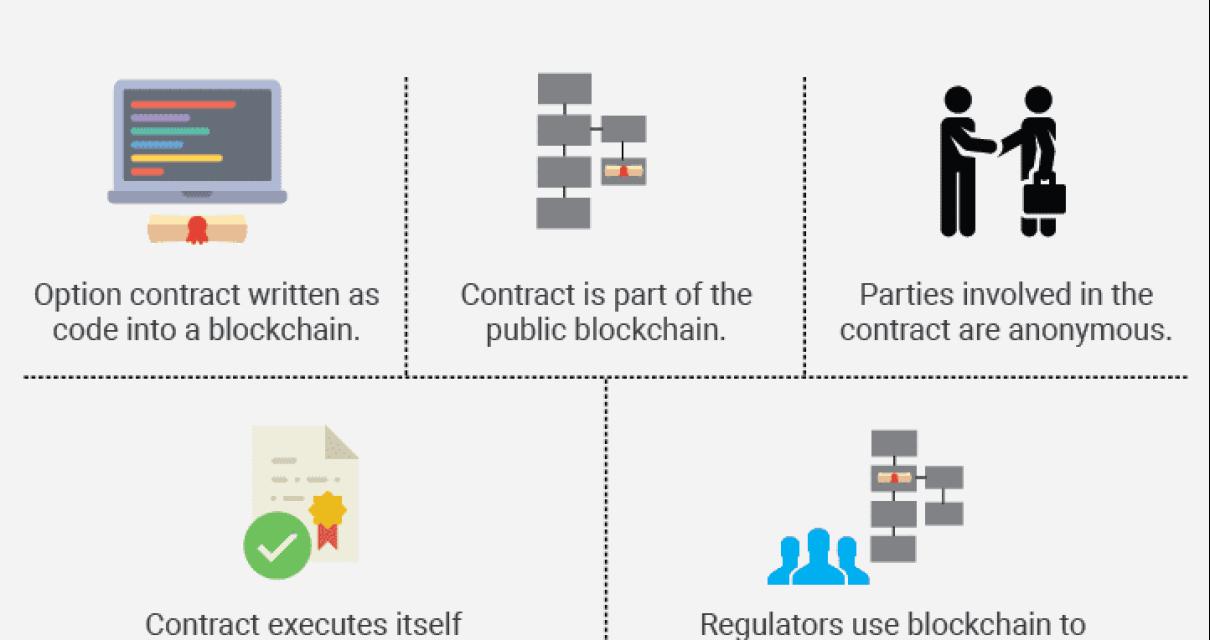
How does a smart contract blockchain work?
A smart contract blockchain is a distributed database that maintains a continuously growing list of digital contracts. Contracts are digital agreements that are enforced and recorded using blockchain technology. When a party to a contract executes the terms of that contract, the blockchain technology ensures that the terms of that agreement are carried out.
What are the advantages of a smart contract blockchain?
Some of the advantages of a smart contract blockchain are that it is tamper-proof and immutable. Additionally, it can be used to create a distributed ledger that can be used for tracking assets and transactions.
What are the disadvantages of a smart contract blockchain?
There are a few potential disadvantages of using a smart contract blockchain. One potential disadvantage is that a smart contract blockchain may not be able to handle large numbers of transactions. Another potential disadvantage is that a smart contract blockchain may be less secure than other types of blockchain networks.
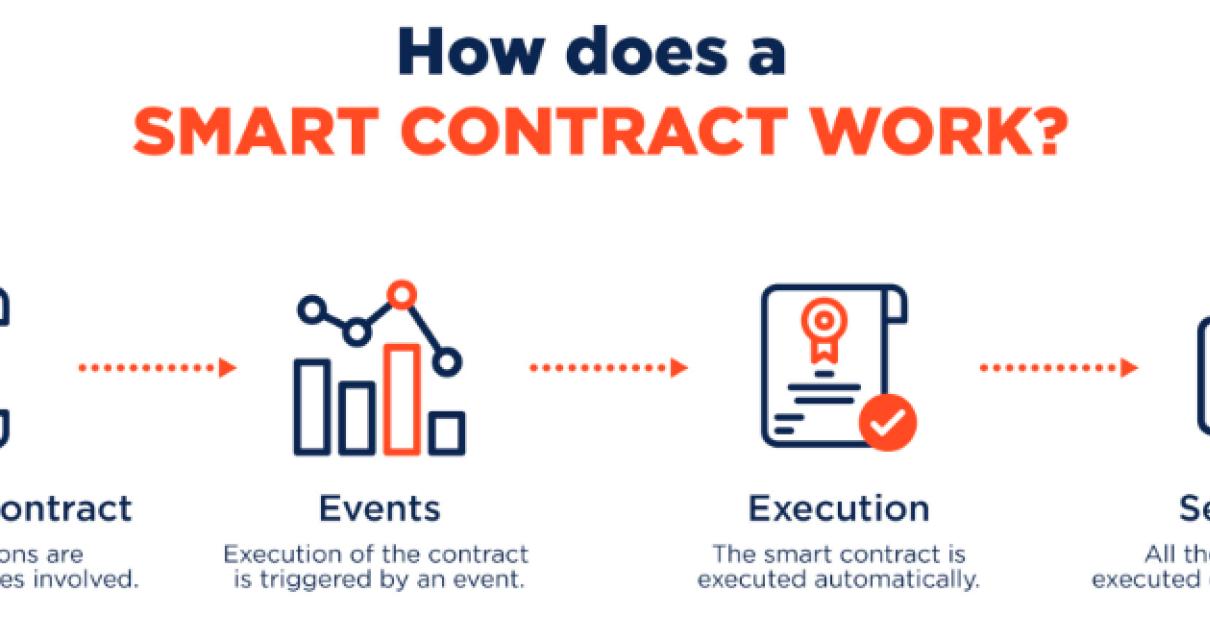
How can businesses use a smart contract blockchain?
A business can use a smart contract blockchain to create a secure, transparent and permanent record of agreements between parties. Smart contract blockchains can also be used to manage transactions and enforce contracts.
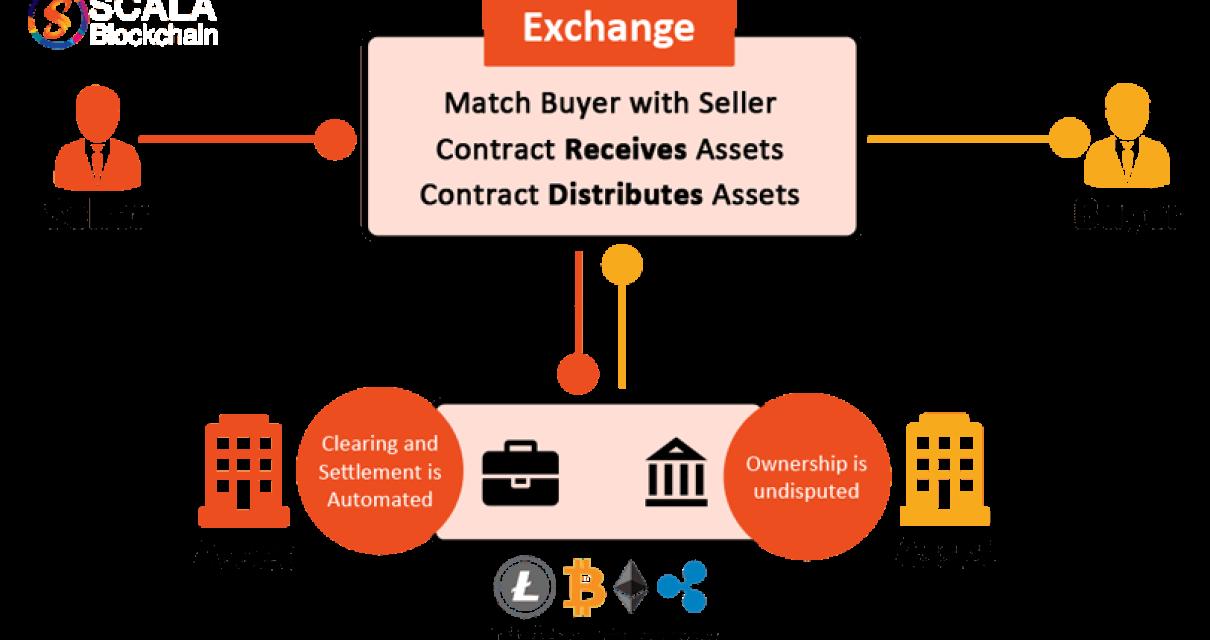
What are some potential applications of a smart contract blockchain?
Some potential applications of a smart contract blockchain include:
-E-commerce: A smart contract blockchain could be used to track the shipment of goods between vendors and buyers.
-Supply chains: A smart contract blockchain could be used to track the movement of goods throughout the supply chain.
-Insurance: A smart contract blockchain could be used to manage insurance contracts.
-Financing: A smart contract blockchain could be used to manage financing agreements.
-Digital assets: A smart contract blockchain could be used to manage digital assets, such as music, video, and software.
What challenges must be addressed before widespread adoption of a smart contract blockchain?
There are a number of challenges that need to be addressed before widespread adoption of a smart contract blockchain. These include the following:
-Smart contract technology is still in its early stages and needs to be improved in order to be more user-friendly.
-There is currently no standard way to build or deploy smart contracts on a blockchain, which can make it difficult for businesses to adopt the technology.
-The security of smart contracts remains a concern, as hackers could potentially exploit vulnerabilities in the code.
-The overall scalability of a blockchain platform is also an issue, as it can be difficult to scale up the network to accommodate a large number of transactions.