What is the difference between layer 1 and layer 2 blockchain?
Layer 1 blockchain is a distributed ledger that contains the history of all transactions. Layers 2 and 3 are the underlying technologies that make layer 1 possible. Layers 2 and 3 provide the security, performance, and scalability needed for widespread adoption of blockchain technology.
What are the benefits of layer 2 blockchain?
Layer 2 blockchain offers a number of benefits, including the following:
1. Increased scalability. Because layer 2 blockchain networks are not led by a single entity, they can achieve a much higher level of scalability than traditional centralized systems. This means that layer 2 blockchain networks can process more transactions than traditional centralized systems without compromising the security of information.
2. Increased security. Because layer 2 blockchain networks are decentralized, they are less susceptible to malicious attacks. In addition, because each node in a layer 2 blockchain network is responsible for maintaining its own copy of the ledger, the network is resistant to data tampering.
3. increased transparency. Because layer 2 blockchain networks are transparent, everyone participating in the network can see the transactions taking place. This increases transparency and accountability, which can lead to increased trust and confidence in the network.
4. reduced costs. Because layer 2 blockchain networks are decentralized, they require less resources to operate than traditional centralized systems. This reduces the costs associated with operating a layer 2 blockchain network, which can lead to increased adoption and utilization of the network.
How does layer 2 blockchain work?
Layer 2 blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that operates on a peer-to-peer basis. Transactions are verified by network nodes and then recorded in a distributed ledger. Nodes can be computers that are running the bitcoin software, or other nodes that are running a different software. Transactions are verified by network nodes and then recorded in a distributed ledger. Nodes can be computers that are running the bitcoin software, or other nodes that are running a different software.
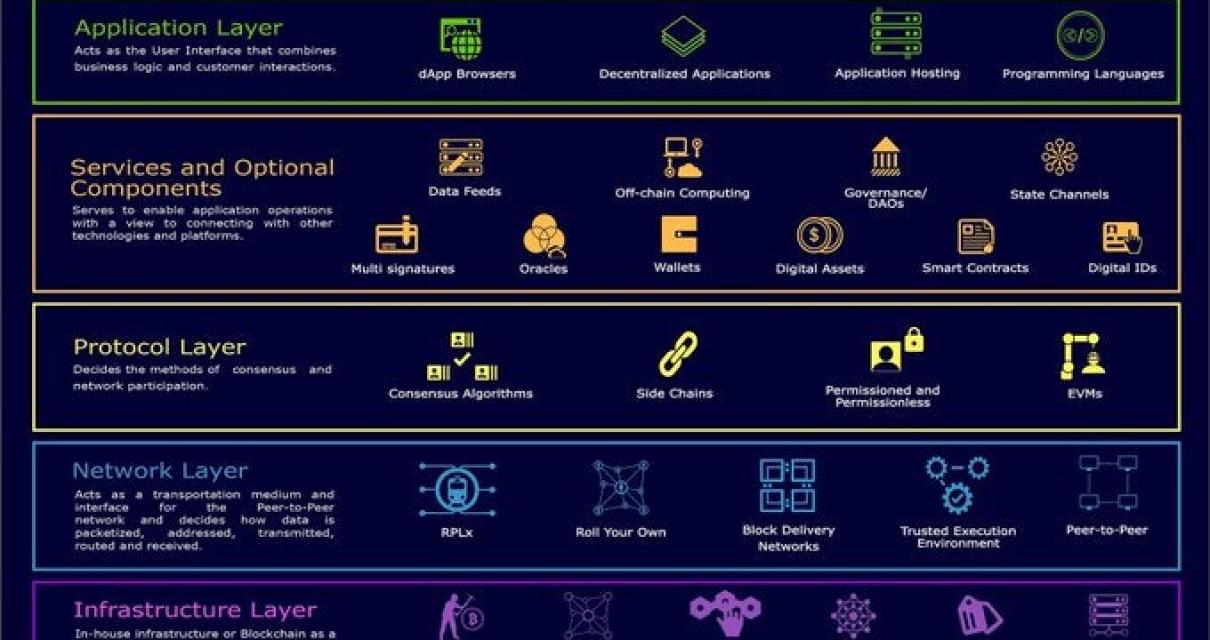
What is the future of layer 2 blockchain?
There is potential for layer 2 blockchain to become a more popular technology, as it offers a number of advantages over traditional blockchain technology. These advantages include the ability to scale up and down, as well as the ability to operate in a more decentralized manner. Additionally, layer 2 blockchain could be particularly useful in areas such as shipping and supply chains, where transparency and efficiency are key priorities.
Why is layer 2 blockchain important?
Layer 2 blockchain technology is important because it allows for decentralized applications to be built on top of it. Decentralized applications are applications that are powered by a network of users and not by a single entity. This is different from traditional applications, which are typically run by a single entity such as a company or government.
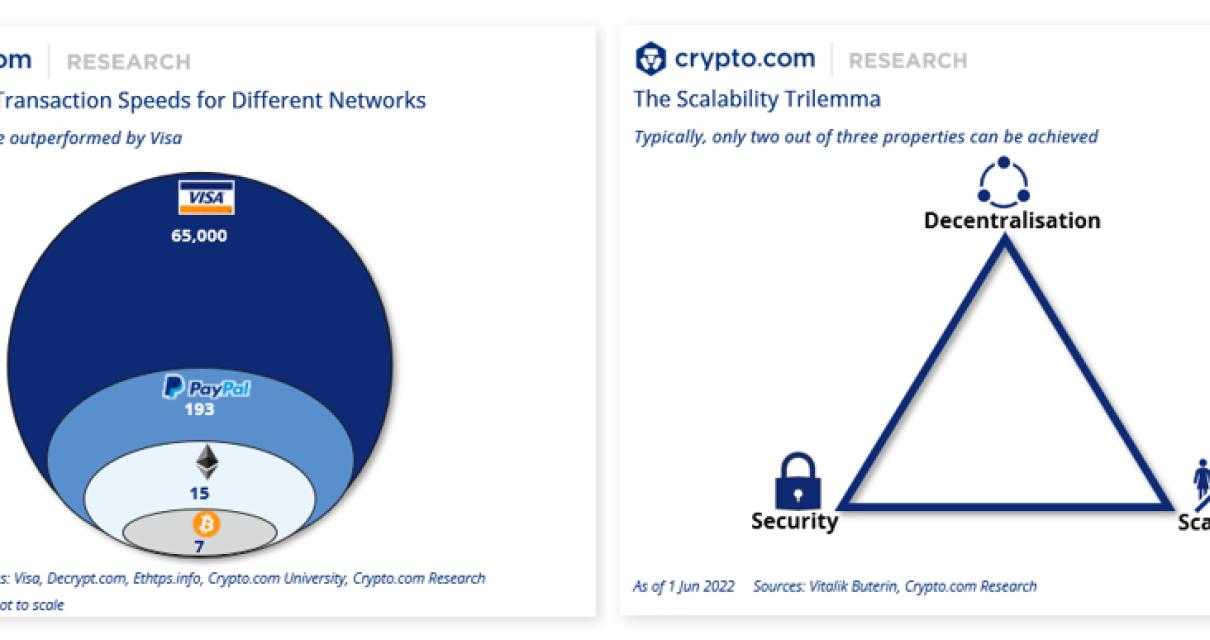
What are the challenges of layer 2 blockchain?
Some of the challenges of layer 2 blockchain technology include scalability, security, and governance. Additionally, layer 2 blockchain technology is still in its early stages, so there are still some unanswered questions about how it will work in practice.
What is the difference between layer 1 and layer 2 blockchain technology?
Layer 1 blockchain technology is a distributed database that maintains a continuously growing list of transactions. Each node in the network updates its copy of the ledger, but no single node has a complete copy. This makes it possible to verify the legitimacy of a transaction without needing to access the full ledger.
Layer 2 blockchain technology is a distributed ledger that allows multiple parties to simultaneously update and agree on the state of a database. Transactions are verified by consensus rather than by a centralized authority.
What are the benefits and challenges of layer 2 blockchain technology?
Layer 2 blockchains offer a number of benefits over traditional blockchain technology, including:
- Reduced data storage and processing requirements: Because layer 2 blockchains are built on top of existing networks, they require far less storage space than traditional blockchains. In addition, layer 2 blockchains can process transactions more quickly than traditional blockchains because they don't require miners to solve complex mathematical equations.
- Increased flexibility and scalability: Because layer 2 blockchains are built on top of existing networks, they can easily be expanded and upgraded to handle more transactions. In contrast, traditional blockchains are designed to be completely decentralized and unchangeable.
- Security benefits: Layer 2 blockchains are typically more secure than traditional blockchains because they are not as open to attack. For example, a malicious actor who wants to break into a layer 2 blockchain would need to access the underlying network and corrupt the data. This is much harder than attacking a traditional blockchain, which is accessible to anyone with an internet connection.
- Reduced costs: Because layer 2 blockchains are built on top of existing networks, they typically require less infrastructure than traditional blockchains. For example, a layer 2 blockchain that is built on top of the Ethereum network requires only a small amount of computing power to run.
- Greater transparency: Because layer 2 blockchains are built on top of existing networks, they are typically more transparent than traditional blockchains. This means that everyone who participates in a layer 2 blockchain can see all of the transactions that have taken place on the network.

What is the future of layer 1 and layer 2 blockchain technology?
Layer 1 blockchain technology is used to store and manage data on a decentralized network. It is used in applications such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, and ripple. Layer 2 blockchain technology is used to manage transactions on a decentralized network. It is used in applications such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, and ripple.