What is a layer one blockchain?
Layer one blockchains are the most basic form of blockchains. They are typically used for small to medium sized businesses. These blockchains are not as secure as other types of blockchains and they are not as widely used.
A primer on layer one blockchain technology
Layer one blockchain technology is a distributed ledger that records the transactions of digital assets and smart contracts. Transactions are verified and recorded in a chronological order, and each node in the network maintains a copy of the ledger.
This technology can be used to create a tamper-proof record of asset ownership and to automate complex business processes. It can also be used to create a digital asset exchange platform, or to facilitate peer-to-peer transactions.
Layer one blockchain technology is not suitable for storing large amounts of data, and it is not suitable for performing high-volume transactions.
An overview of layer one blockchain technology
Layer one blockchain technology refers to the foundational blockchain technology that supports decentralized applications and Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT).
Layer one blockchain technology is a distributed ledger that maintains a continuously growing list of ordered transactions. Transactions are grouped into blocks and chained together using cryptography. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data.
Each node on the network updates its copy of the blockchain with each new block. Nodes that don’t have a copy of the blockchain can’t participate in the network.
Layer one blockchain technology provides a tamper-resistant, transparent and secure record of transactions. It’s also resistant to attack because it uses cryptography to protect against unauthorized changes.
Layer one blockchain technology can be used to track assets, monitor transactions and create a digital ledger of ownership for anything that can be represented as a series of transactions.

The basics of layer one blockchain technology
Layer one blockchain technology is the most basic form of blockchain technology. It is a distributed database that maintains a continuously growing list of records, called blocks, which are linked together by cryptography. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. Transactions are verified by network nodes and then added to the block chain. Bitcoin is the first and most well-known example of a layer one blockchain.
How layer one blockchain technology works
A blockchain is a distributed database that maintains a continuously growing list of records, called blocks. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. Bitcoin and most other blockchain implementations use a proof-of-work algorithm to generate new blocks. Bitcoin nodes use the block chain to differentiate legitimate Bitcoin transactions from attempts to re-spend coins that have already been spent elsewhere.
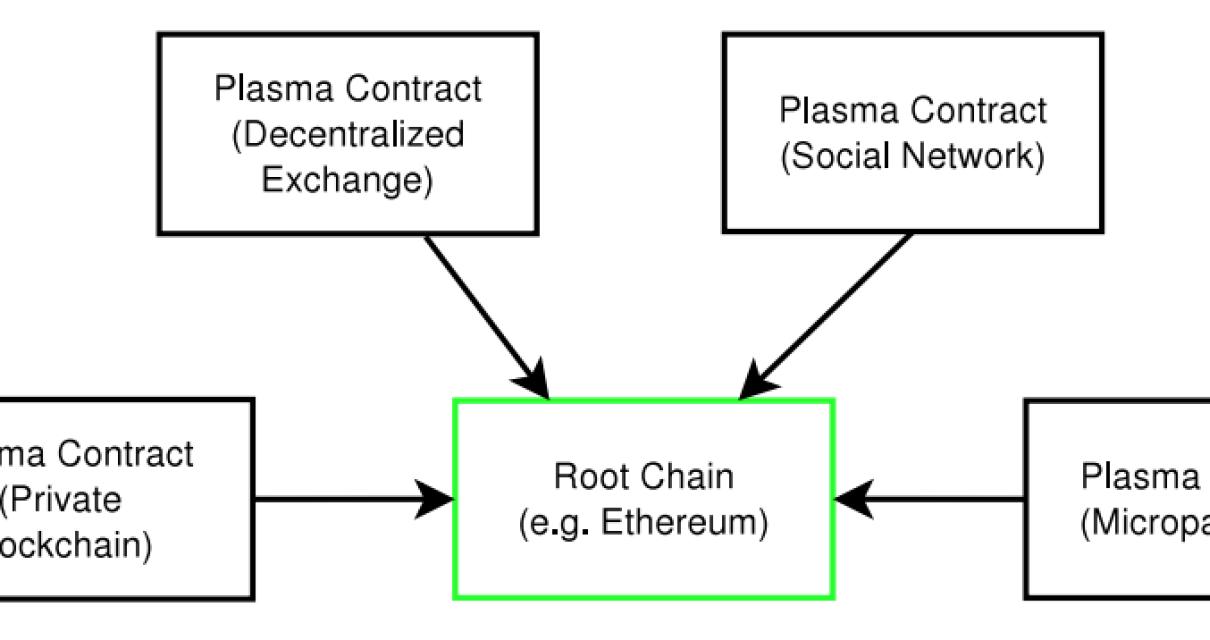
The benefits of layer one blockchain technology
Layer one blockchain technology is a distributed ledger technology that enables secure, transparent and tamper-proof recordkeeping. Transactions are verified and enforced by network nodes through cryptography and recorded in a chronological order. This makes it difficult for anyone to tamper with the records or to make unauthorized changes.
Layer one blockchains are often more efficient than other blockchain technologies because they don’t require a large number of participants to operate. This makes them well-suited for use cases such as digital asset management, supply chain management and financial services.
Layer one blockchains also have the potential to improve trust relationships between different parties. This is because they can provide a tamper-proof record of transactions that can be used to prove the legitimacy of a transaction or to show that a party is in compliance with a contract.
Finally, layer one blockchains could be used to create decentralized applications (dApps). These are applications that run on a network of nodes and use blockchain technology to enable users to interact with each other without the need for a third party.
The potential of layer one blockchain technology
Layer one blockchain technology is a distributed database that can store any type of information. This technology can be used to create a secure and transparent ledger of transactions. This system can be used to track the ownership of assets, and it can also be used to manage contracts.
The challenges of layer one blockchain technology
Layer one blockchain technology is still in its early developmental stages, meaning that there are a number of challenges that need to be overcome in order for it to become a mainstream technology.
One of the biggest challenges is that layer one blockchain technology is not able to handle high transaction volumes. This is because it is not able to process large numbers of transactions quickly enough, which can cause delays and potential problems.
Another challenge is that layer one blockchain technology is not secure. This is because it is not able to protect information effectively, which could lead to data breaches and other security issues.
Finally, layer one blockchain technology is not widely accepted yet. This means that it is not widely used by businesses or governments, which can make it difficult to scale up and achieve widespread adoption.
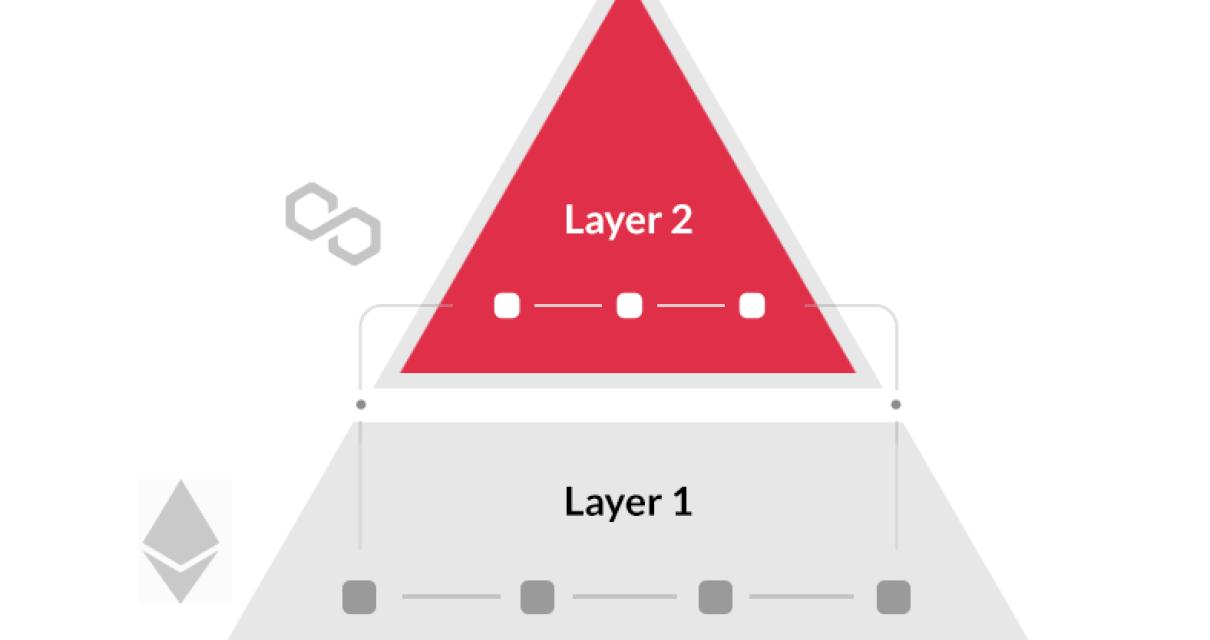
The future of layer one blockchain technology
Layer one blockchain technology, also known as the “parent chain,” is the foundational layer of a blockchain network. It serves as a secure and transparent record of all transactions that occur on the network.
As layer one technology matures, it could play an important role in expanding the potential uses for blockchains.Layer one blockchain technology could be used to create tamper-proof digital certificates, create immutable ledgers for tracking assets, and create secure voting systems.
As layer one technology continues to evolve, it could become an important tool for businesses and governments to use in their efforts to secure and track data.
Why layer one blockchain technology is important
?
Layer one technologies allow for the interoperability of blockchain networks. They provide a way for different blockchain networks to communicate with one another and share information. This allows different blockchain networks to work together and share resources.