Discovering the Blockchain Network
The first step in understanding the blockchain network is to understand how it works. The blockchain network is a distributed database that contains a list of all the transactions that have ever taken place. Each node in the network stores a copy of the blockchain database.
To make a new transaction, a user first needs to find an existing transaction that they want to modify. They can do this by using a search engine, scanning through the blockchain database, or by looking for transactions that have been tagged with a certain keyword.
Once they have found the transaction they want to modify, they need to find the block number for that transaction. The block number is a unique identifier for each block in the blockchain database.
Next, they need to find the hash value for the block number. The hash value is a unique number that is generated when the block is created.
Finally, they need to find the transaction data for the block number. The transaction data contains all the information about the transaction, including the sender, the receiver, and the amount of money that was transferred.
Once they have all of the information they need, they can start to make their modifications. They can change the sender, receiver, or amount of money that was transferred. They can also add new transactions to the blockchain database.
Once they have finished making their modifications, they need to save them to the blockchain network. They can do this by using a blockchain application programming interface (API) or by writing code that will automatically save the changes to the blockchain network.
There are a number of different ways that users can interact with the blockchain network. The most common way is to use blockchain applications. Blockchain applications are software programs that use the blockchain network to store and manage data.
Blockchain applications are used to store data such as financial records, medical records, and digital certificates. They are also used to manage transactions and to create smart contracts.
Blockchain applications can be used by businesses of all sizes. They can be used to store data for internal use, or they can be used to store data for public consumption.
The blockchain network is still in its early stages. There are a number of issues that needs to be addressed before it can be used on a large scale. Some of these issues include scalability and security. However, overall, the blockchain network is proving to be very resilient and reliable.
What is the Blockchain Network?
A blockchain network is a decentralised network of computers that maintain a continuously growing list of records, called blocks, which are linked and secured using cryptography. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. Bitcoin, the first and most well-known example of a blockchain network, uses the SHA-256 hashing algorithm.
How the Blockchain Network Works
The Bitcoin network is a peer-to-peer payment network that operates on a cryptographic protocol. Transactions are verified by network nodes through cryptography and recorded in a public dispersed ledger called a blockchain. Bitcoin was invented by an unknown person or group of people under the name Satoshi Nakamoto[1] and released as open-source software in 2009.
Each node operates in a distributed manner, with data collected from participating nodes spread across a global network. Bitcoin nodes use the block chain to differentiate legitimate Bitcoin transactions from attempts to re-spend coins that have already been spent elsewhere. Bitcoin nodes use the block chain to distinguish legitimate Bitcoin transactions from attempts to re-spend coins that have already been spent elsewhere.
Bitcoin nodes use the block chain to distinguish legitimate Bitcoin transactions from attempts to re-spend coins that have already been spent elsewhere. Bitcoin nodes use the block chain to distinguish legitimate Bitcoin transactions from attempts to re-spend coins that have already been spent elsewhere. The Bitcoin network requires a proof of work to be validated and added to the block chain for every new block created. This proof of work is accomplished by solving a difficult mathematical problem.
Nodes can agree to use a proof-of-work scheme based on a certain difficulty target. When a node discovers a new block, it broadcasts the block to all nodes. Each node then tries to create a new block that contains the proof-of-work of the previous block, including the solved difficulty target. If a node fails to generate a new block within a set period of time, it is considered to have failed the proof-of-work requirement and will not add its share of the block chain to its memory.
The Benefits of the Blockchain Network
There are a number of benefits that can be derived from using the blockchain network. These benefits include:
Security: The blockchain network is extremely secure, and there is no way to tamper with the data stored on it. This is because the blockchain network is based on a distributed database system.
Transparency: The blockchain network is transparent, meaning everyone can track the transactions that take place on it. This is because the blockchain network uses a public ledger.
Immutability: The blockchain network is immutable, meaning that once a transaction has been recorded on the blockchain network, it cannot be changed.
Efficiency: The blockchain network is highly efficient, meaning that it can process a large number of transactions quickly. This is because the blockchain network is based on a peer-to-peer network.
Low cost: The blockchain network is low cost, meaning that it is not expensive to operate. This is because the blockchain network does not require expensive infrastructure to be set up, like traditional financial institutions do.
The blockchain network has a number of other benefits as well, including:
Decentralization: The blockchain network is decentralized, meaning that it is not controlled by any single entity. This is a major advantage over traditional financial institutions, which are often controlled by a few large entities.
Trust: The blockchain network is based on trust, which is a major factor in its success. Because people trust the blockchain network, they are more likely to use it to conduct transactions.
Anonymity: The blockchain network is anonymous, meaning that users can remain anonymous when conducting transactions on it. This is an advantage over traditional financial systems, which require users to provide their personal information.
The blockchain network has a number of potential applications, including:
The blockchain network can be used to create a digital ledger of all transactions that take place on it. This can be used to track the movement of money, assets and other valuable items.
The blockchain network can be used to create a digital ledger of all transactions that take place on it. This can be used to track the movement of money, assets and other valuable items. The blockchain network can be used to create a digital registry of property rights. This could be used to track the ownership of land, property and other valuable assets.
The blockchain network can be used to create a digital registry of property rights. This could be used to track the ownership of land, property and other valuable assets. The blockchain network can be used to create a digital identity system. This could be used to identify individuals and track their movements.
The blockchain network has a number of potential applications, including:
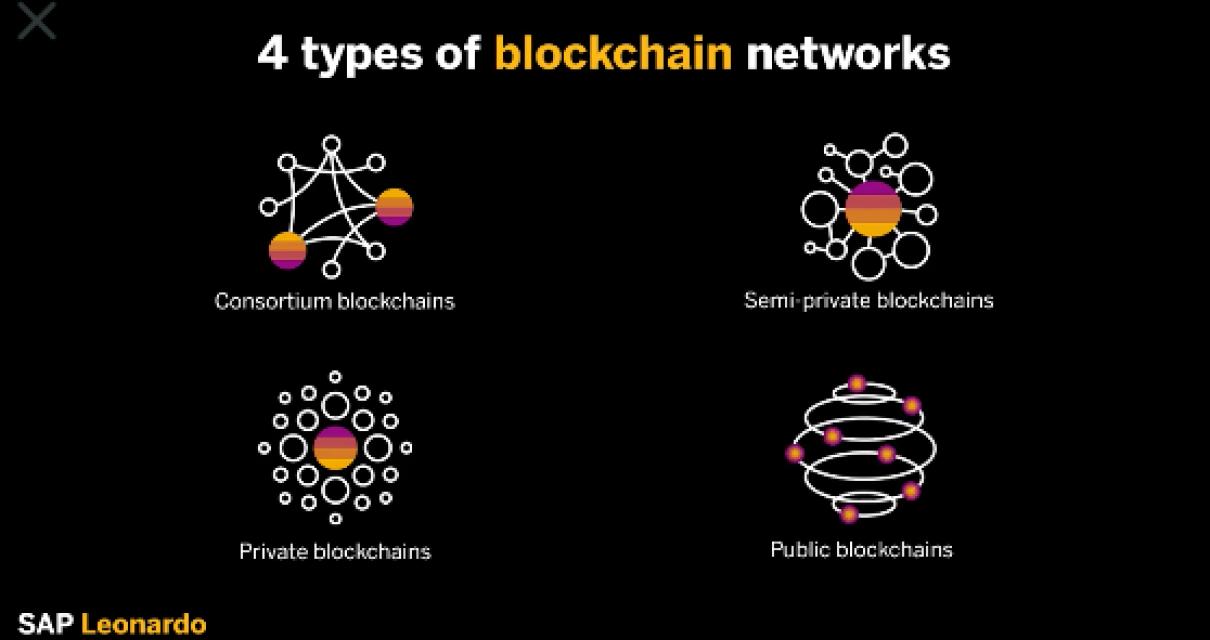
The Future of the Blockchain Network
The future of the blockchain network is still up for debate, but there are a few potential outcomes that could happen.
One possibility is that the blockchain network will become more centralized over time. This could happen because a few large companies or governments manage to gain a controlling stake in the network, leading to a more centralized system.
Another possibility is that the blockchain network will become more decentralized, with a greater number of nodes participating. This could happen because individuals and companies find the blockchain network more advantageous and decide to invest in it, increasing its decentralization.
Ultimately, the future of the blockchain network is still up for debate, but there are some potential outcomes that could happen.
The Evolution of the Blockchain Network
Since the inception of blockchain technology in 2009, the network has undergone a number of changes. In this article, we will explore the history of the blockchain network and highlight some of the key milestones.
2009-2012: Early Development
The genesis block of the blockchain network was created on January 3, 2009. This block contained the genesis transactions, which introduced the concept of a distributed ledger. At the time, this was an innovative idea that could not be implemented using traditional database systems.
2012-2015: Expansion
In 2012, the first cryptocurrency, bitcoin, was created. Bitcoin was based on the blockchain network, and it was the first application of this technology. As the popularity of bitcoin grew, so did the popularity of the blockchain network.
2015-2016: The Fork
On August 1, 2015, bitcoin and bitcoin cash were created as a result of a fork in the blockchain network. Bitcoin cash was designed to be more user-friendly than bitcoin, and it quickly became a popular cryptocurrency.
2016-present: Growth
Since 2016, the blockchain network has experienced significant growth. This growth has been driven by the increasing popularity of cryptocurrencies such as bitcoin and Ethereum. In addition, the blockchain network has been used to create other innovative applications, such as smart contracts and decentralized applications.
The Impact of the Blockchain Network
A blockchain network is a distributed database that maintains a continuously growing list of ordered records, called blocks. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. Bitcoin and other digital currencies are based on a blockchain network.
Each block in the blockchain is linked to the block that came before it, forming a chain. This chain of blocks is constantly growing as “completed” blocks are added to it with a new set of transactions. Each block can have a different number of transactions, and the order of those transactions is not guaranteed.
Because blockchains are decentralized, they are immune to cyberattacks and data manipulation. This makes them an attractive platform for applications that require trustless transactions, such as smart contracts and cryptocurrencies.

The Potential of the Blockchain Network
There are many potential applications for the blockchain network. Some of these include:
1. Financial Services
The blockchain network could be used to create a digital ledger of financial transactions that is tamper-proof. This would make it easier for companies to track their finances and prevent fraudulent activities.
2. Supply Chain Management
The blockchain network could be used to manage supply chains more efficiently. This would make it easier for companies to track their products from source to sale, and ensure that they are receiving the correct amount of ingredients and materials.
3. Identity Management
The blockchain network could be used to manage identity documents. This would make it easier for people to verify their identity online and access essential services without having to provide personal information.
4. Voting Systems
The blockchain network could be used to create secure voting systems. This would make it easier for people to cast their votes without fear of fraud or tampering.
5. Cryptocurrency Trading
The blockchain network could be used to create a digital marketplace for the trading of cryptocurrencies. This would make it easier for people to buy and sell cryptocurrencies without having to deal with complex financial transactions.
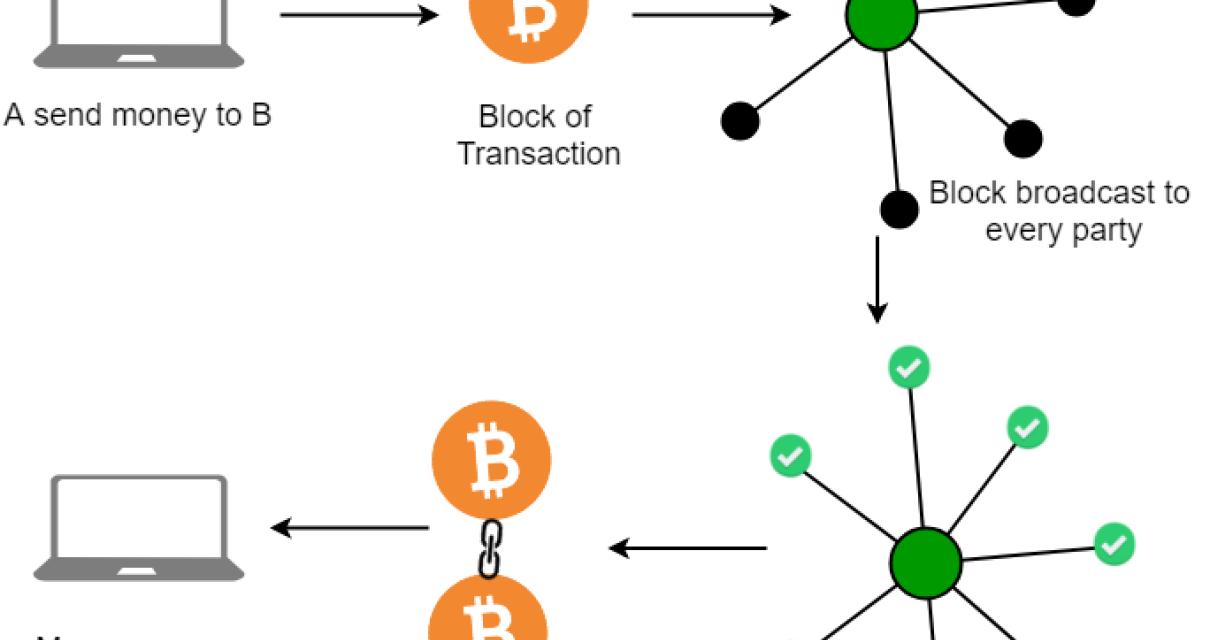
The Applications of the Blockchain Network
There are a number of potential applications for the blockchain network, including but not limited to:
1. Property records - A blockchain network could be used to track property ownership and transactions.
2. Contracts - A blockchain network could be used to track and manage contracts.
3. Voting - A blockchain network could be used to track and manage votes.
4. Finance - A blockchain network could be used to track and manage financial transactions.
5. Health records - A blockchain network could be used to track and manage health records.
The Limitations of the Blockchain Network
There are some limitations to the blockchain network that should be considered. First, the blockchain network is not without its own flaws. For example, there have been reports of blockchain networks being hacked, with coins and other assets being stolen. Additionally, the blockchain network is not able to handle large volumes of transactions quickly or efficiently.
Another limitation to consider is that the blockchain network is not regulated by any governing body. This means that the blockchain network is not subject to the same regulations as other financial systems. This could lead to problems if the blockchain network is used for financial transactions that are considered to be risky or illegal.
The Benefits and Limitations of the Blockchain Network
The blockchain network has many benefits, including:
1. Transparency: The blockchain network is transparent, meaning everyone can see how many bitcoins are being transferred and who is sending them. This transparency makes the blockchain network an effective way to prevent fraud and other illegal activities.
2. Immutability: The blockchain network is immutable, meaning it is impossible for anyone to change or delete any of the information stored on it. This feature makes the blockchain network an effective way to track and record transactions.
3. Security: The blockchain network is highly secure, meaning it is difficult for anyone to tamper with the information stored on it. This feature makes the blockchain network an effective way to protect against fraudulent activities.
4. Cost effectiveness: The blockchain network is cost effective, meaning it is easier and less expensive to use than other forms of data storage. This feature makes the blockchain network an attractive choice for businesses and other organizations.