What is layer 1 and layer 2 in blockchain?
Layer 1 is the protocol layer that provides the foundation for the blockchain. It includes rules for how transactions are verified and shared, as well as a distributed ledger of all transactions. Layer 2 is the application layer that implements these protocols on a specific platform.
Layer 1 and layer 2 explained
Layer 1 is the bottommost layer of the OSI model and it is responsible for transporting data between the application and the network. Layer 1 can be divided into two sublayers, the physical layer and the data link layer. The physical layer deals with the transmission of signals between devices, while the data link layer provides the necessary mechanisms for managing the exchange of data.
Layer 2 is the second layer of the OSI model and it provides the necessary mechanisms for managing the communication between devices. Layer 2 can be divided into two sublayers, the network layer and the transport layer. The network layer provides the necessary mechanisms for routing packets between devices, while the transport layer provides the necessary mechanisms for carrying data.
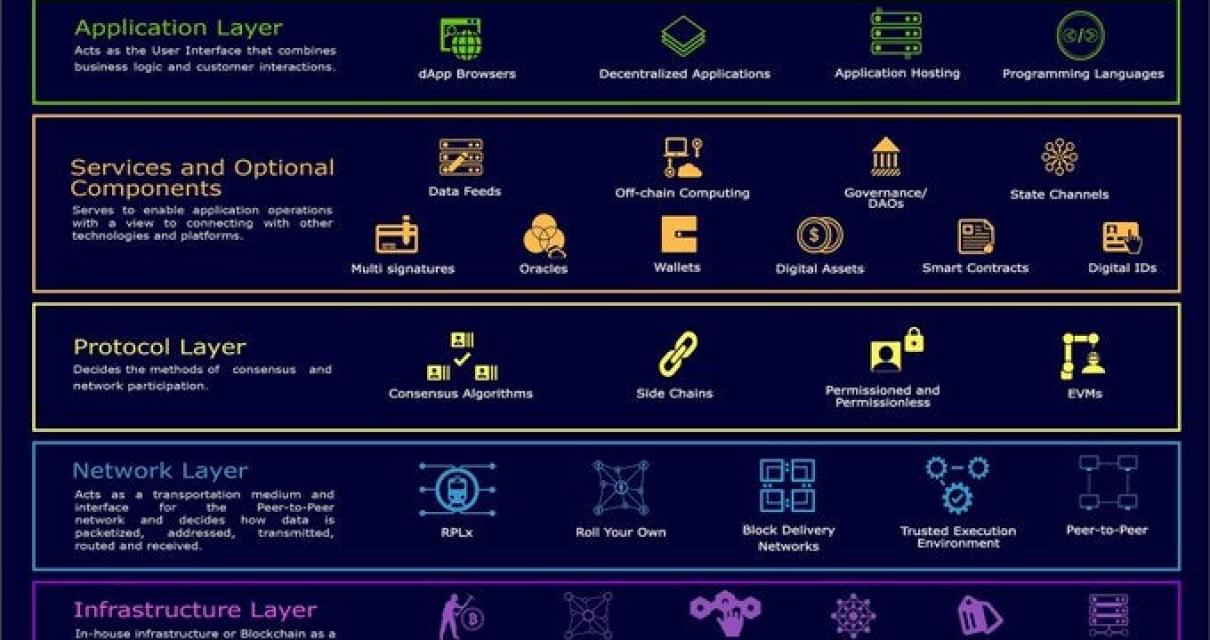
The difference between layer 1 and layer 2
Layer 1 is the bottommost layer of the OSI model and corresponds to the physical layer. Layer 1 provides a connection between devices on the network and delivers data packets. Layer 1 also handles errors that occur during transmission.
Layer 2 is the second layer of the OSI model and corresponds to the network layer. The network layer establishes and maintains connections between devices on the network. It also manages the flow of data packets between devices.
Layer 3 is the third layer of the OSI model and corresponds to the application layer. The application layer provides an interface between devices and the network. It also handles the requests of users and applications on the network.
What are the benefits of layer 1 and layer 2?
Layer 1 is responsible for the data that is visible to the user. Layer 2 is responsible for the data that is not visible to the user.
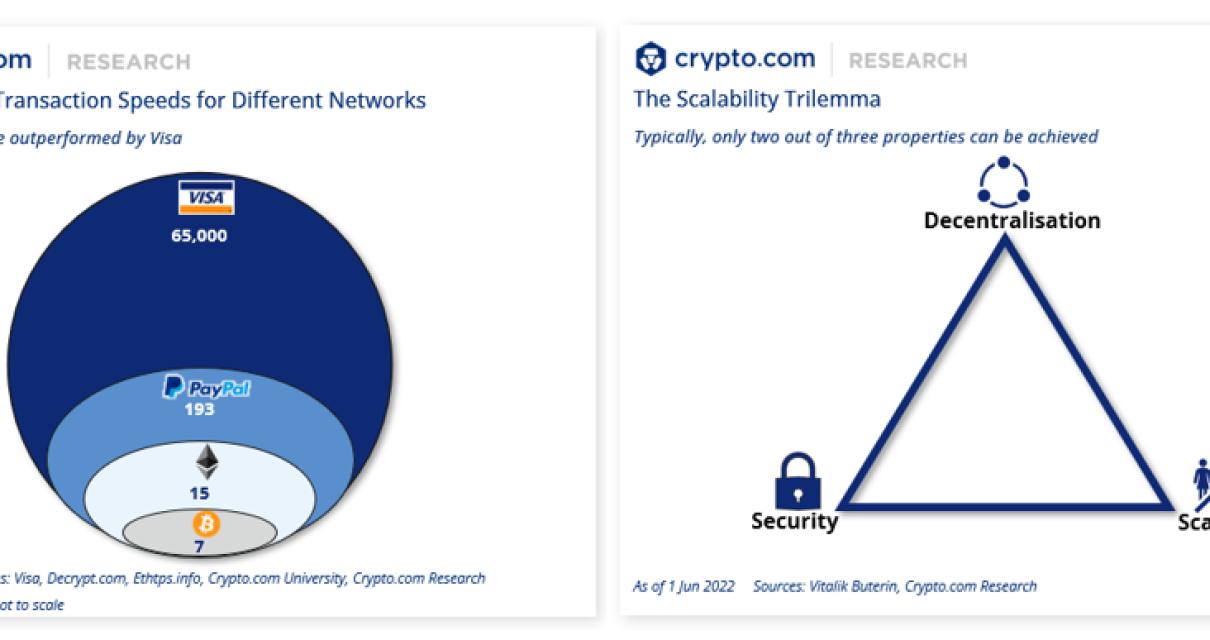
How do layer 1 and layer 2 work together?
Layer 1 is responsible for the initial identification of what is on the screen and then passes that information along to layer 2. Layer 2 then provides the actual image that is displayed on the screen.
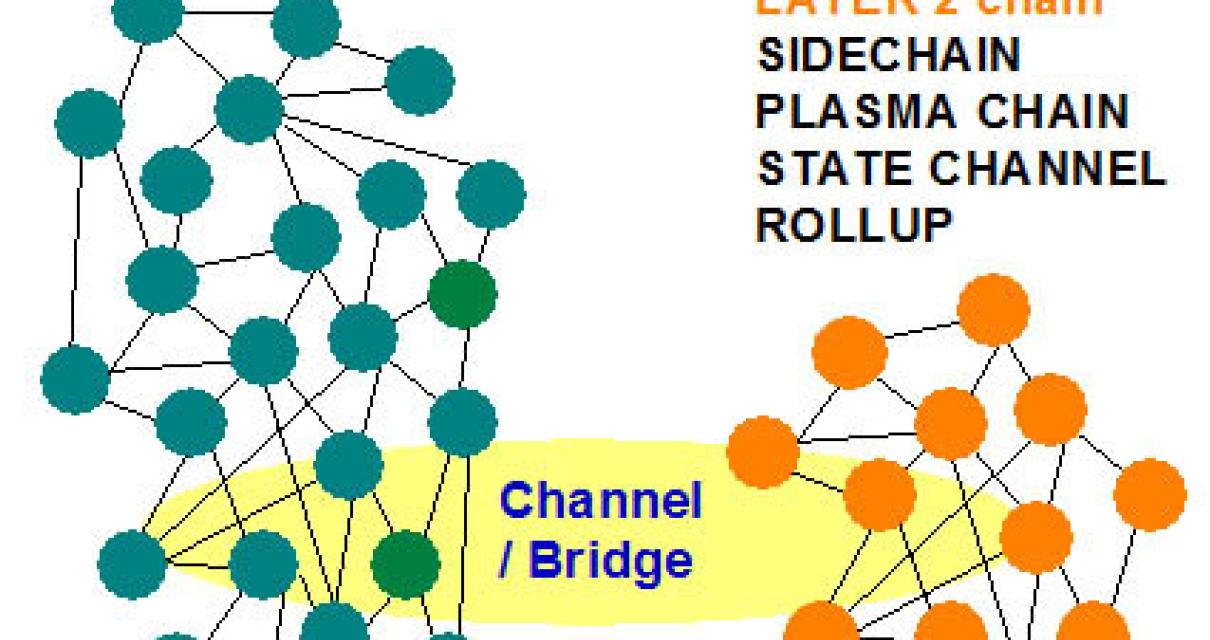
What are the challenges of implementing layer 1 and layer 2?
Layer 1 is the lowest level of the OSI model and it handles the packet-level data. Layer 2 is the next layer up and it handles the circuit-level data. The challenge with layer 1 is that it is not always possible to trust the data that is being sent through the network. Layer 2 can help to ensure the data is legitimate, but it can also be more expensive to implement.
A guide to understanding layer 1 and layer 2
Layer 1 is the lowest layer of the OSI model and is responsible for the transmission of data. It consists of the physical layer, the link layer, and the network layer. Layer 2 is the next layer up and is responsible for the transmission of packets. It consists of the MAC (media access control) layer, the PHY (physical layer), and the IP (internet protocol) layer.
The pros and cons of layer 1 and layer 2
Layer 1 is the most visible layer of the OSI model. It provides the user interface and interacts with the user. Layer 2 provides the underlying infrastructure for layer 1, such as transmission control protocol/Internet protocol (TCP/IP) and network interface control protocol/Internet protocol (NIC/IP).
Layer 1 can be vulnerability-prone because it is exposed to the user. For example, if a user clicks on a link in an email that takes them to a website that contains a malicious file, the file could be downloaded and executed on the user's computer.
Layer 2 can be more secure because it is protected by the firewall and other security measures. For example, if a user clicks on a link in an email that takes them to a website, the website might request authentication before allowing the website to load.
What are the implications of layer 1 and layer 2?
Layer 1 is the physical layer of the OSI model. It encompasses the transmission of data packets between devices and the physical connection between those devices. Layer 2 is the uppermost layer of the OSI model and deals with the routing and delivery of packets.
Why islayer 1 and layer 2 important?
Layer 1 is important because it provides the basic structure for the network. Layer 2 provides the necessary security and routing for the network.
How can blockchain be used with layer 1 and layer 2?
Blockchain technology can be used with both layer 1 and layer 2 protocols. Layer 1 protocols include the traditional TCP/IP networking protocol, while layer 2 protocols include the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP). When using blockchain technology with layer 1 protocols, it can be used to create a distributed ledger of transactions. This can be used to track the movement of digital assets and other data. When using blockchain technology with layer 2 protocols, it can be used to create a secure network between two parties. This can be used to create a platform for exchanging information.
What are some examples oflayer 1 and layer 2 applications?
Some examples of layer 1 and layer 2 applications are: a website, an email client, a file sharing service, and a messaging app.