What is blockchain technology?
Blockchain technology is a distributed database that allows for users to securely share and manage information. Blockchain technology is decentralized, meaning it is not controlled by any one entity. This makes it resistant to cyberattacks and allows for faster, more secure transactions.
The basics of blockchain technology
A blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger of all cryptocurrency transactions. It is constantly growing as “completed” blocks are added to it with a new set of recordings. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. Bitcoin nodes use the block chain to distinguish legitimate Bitcoin transactions from attempts to re-spend coins that have already been spent elsewhere.
Each user can verify the validity of the block chain by checking the cryptographic hash of each block. If a block’s hash does not match that of the most recent block, then the block is considered invalid and is removed from the chain. Bitcoin nodes use the block chain to differentiate legitimate Bitcoin transactions from attempts to re-spend coins that have already been spent elsewhere.
How blockchain technology works
To understand how blockchain technology works, it is important to first understand what a blockchain is. A blockchain is a digital ledger of all cryptocurrency transactions. It is decentralized, meaning that it is not under the control of any one entity. Each block in a blockchain is linked to the block preceding it, forming a chain. This allows for a tamper-proof record of all transactions.
A blockchain network consists of a network of nodes that each maintain a copy of the blockchain. These nodes are spread throughout the network, so that everyone with an internet connection can participate in the blockchain network. When a user wants to make a transaction, they contact a node on the network and provide them with information about the transaction, such as the address of the cryptocurrency they are sending and the address of the cryptocurrency they are receiving. The node then updates its copy of the blockchain with this information.
To complete the transaction, the user must also provide the node with a cryptographic proof that demonstrates that they own the address of the cryptocurrency they are sending and that they are authorized to spend it. The node then sends the transaction to all other nodes on the network, which will then verify that the transaction is valid and add it to their copies of the blockchain. Once the node has added the transaction to its copy of the blockchain, it broadcasts it to all nodes on the network.
Once a node has received the broadcast, it will update its copy of the blockchain with the information about the transaction and then broadcast it to all other nodes on the network. This process will continue until every node on the network has updated its copy of the blockchain with the latest information.
This arrangement allows for a tamper-proof record of all cryptocurrency transactions. Anyone who wants to tamper with a transaction can do so by tampering with one of the nodes on the network, but this would be detectable and would invalidate the tampered-with transaction.
The decentralized nature of a blockchain network makes it difficult for anyone to tamper with a transaction. This is why it is often referred to as a “distributed ledger”.
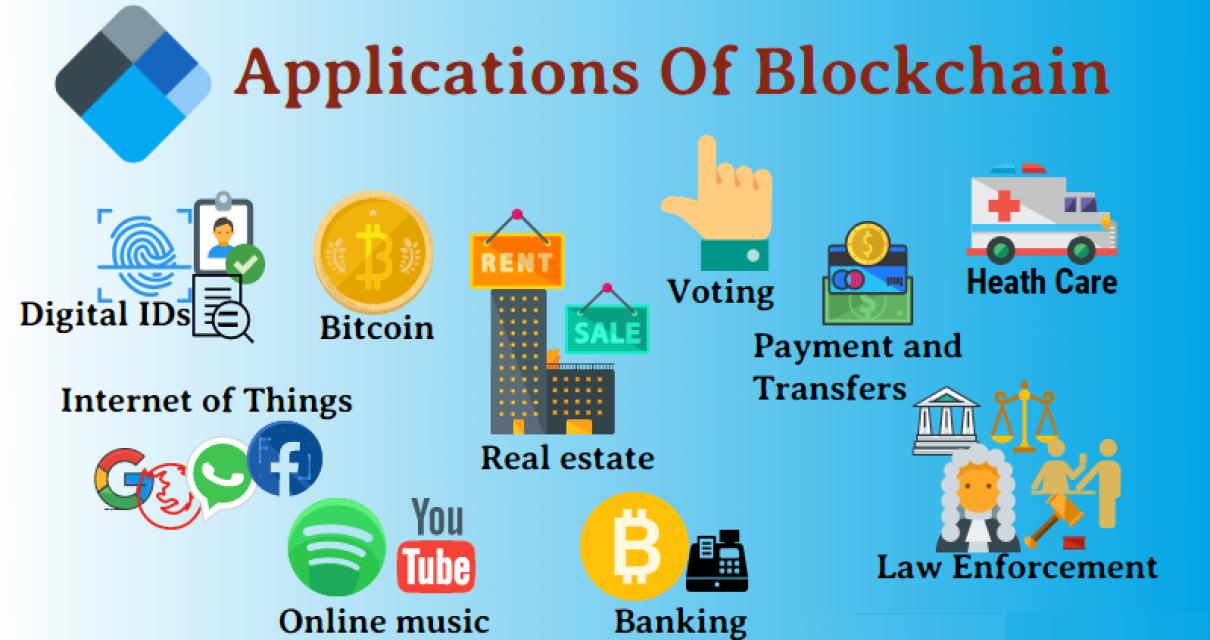
Blockchain technology has many applications, including financial services, supply chains, and online voting. It has been used in experiments to verify the authenticity of digital assets, such as bitcoin.
How does bitcoin work?
Bitcoin works by using cryptography to create a unique digital ID for each bitcoin. This ID is used to track the ownership of each bitcoin. When someone wants to spend bitcoin, they need to provide their digital ID and the associated wallet address to the recipient. The recipient then uses their own digital ID to access the funds and confirms that they own the corresponding wallet address.
Bitcoin is created through a process called “mining”. Miners are rewarded with bitcoin for verifying and confirming transactions on the blockchain network. Bitcoin miners are able to verify and confirm transactions because they are able to access a large number of nodes on the network. This makes it difficult for anyone to tamper with a transaction.
How does blockchain technology work in practice?
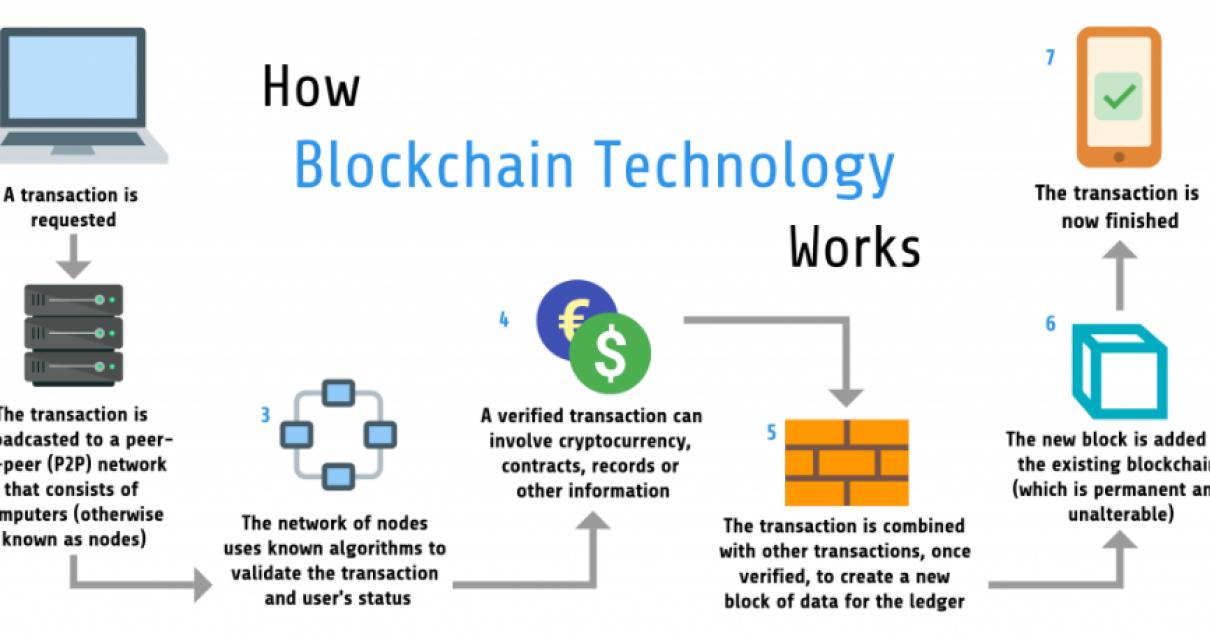
In practice, blockchain technology works like this:
1. A user wants to make a transaction.
2. They contact a node on the network and provide them with information about the transaction, such as the address of the cryptocurrency they are sending and the address of the cryptocurrency they are receiving.
3. The node then updates its copy of the blockchain with this information.
4. To complete the transaction, the user must also provide the node with a cryptographic proof that demonstrates that they own the address of the cryptocurrency they are sending and that they are authorized to spend it.
5. The node then sends the transaction to all other nodes on the network, which will then verify that the transaction is valid and add it to their copies of the blockchain.
6. Once the node has added the transaction to its copy of the blockchain, it broadcasts it to all nodes on the network.
7. Once every node on the network has updated its copy of the blockchain with the latest information, the transaction is completed.
The benefits of blockchain technology
There are many benefits of blockchain technology, including:
1. Transparency: Blockchain is a transparent technology, meaning that everyone can see what is happening on the network. This makes it easier to trust the network and make sure that transactions are legitimate.
2. Security: Blockchain is a secure technology, meaning that it is difficult for people to tamper with the information on the network. This makes it more reliable and secure than other technologies.
3. Immutability: Blockchain is an immutable technology, meaning that once a transaction has been recorded on the network, it cannot be changed. This makes it more reliable and secure than other technologies.
4. Decentralized: Blockchain is a decentralized technology, meaning that there is no one central authority responsible for managing the network. This makes it more democratic and trustable than other technologies.
5. Cost-effective: Blockchain technology is cost-effective, meaning that it is cheaper to use than other technologies. This makes it more affordable and accessible for businesses and consumers.

The potential of blockchain technology
There are many potential applications of blockchain technology, including:
-Distributed ledgers that can improve transparency, accountability and efficiency in financial systems;
-A tamper-proof system for recording and managing transactions;
-A secure way to share information across different networks;
-A mechanism for managing digital identities.
The potential benefits of using blockchain technology are wide-ranging and include increased transparency, security and efficiency.
The risks of blockchain technology
There are a number of possible risks associated with blockchain technology, including the following:
1. Security risks: Blockchain technology is still relatively new and unproven, which could lead to security vulnerabilities.
2. Fungibility risks: Blockchain technology is designed to be highly fungible, which could lead to problems if one cryptocurrency becomes less valuable than others.
3. Centralization risks: Blockchain technology could lead to the concentration of power in the hands of a few entities, which could potentially undermine the decentralization of many other aspects of the system.
4. Lack of liquidity risks: The current market conditions for cryptocurrencies are highly volatile, which could make it difficult for investors to find good investments in blockchain technology.
The future of blockchain technology
There is no doubt that blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize the way we do business. It could help to improve security, transparency, and efficiency across a wide range of industries.
As blockchain technology continues to evolve, it is likely that we will see even more dramatic changes in the way we do business. In the future, it is possible that we will see blockchain technology used to create new forms of digital currencies and other financial products.
Overall, it is clear that blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize the way we do business. However, it will take some time for this technology to fully develop and for its full potential to be realized.