What is Blockchain? A Simple Explanation
Blockchain technology is a distributed database that allows for secure, tamper-resistant transactions. Transactions are verified by network nodes and then recorded in a public ledger. Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies are based on blockchain technology.
What is Blockchain Technology?
Blockchain technology is a distributed database that allows for secure, transparent and tamper-proof transactions. It is also known as a distributed ledger system. Transactions are verified by network nodes and recorded in a public ledger. Each node can independently verify the integrity of the ledger.
What is a Blockchain and How Does it Work?
A blockchain is a digital ledger of all cryptocurrency transactions. It is constantly growing as "completed" blocks are added to it with a new set of recordings. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. Bitcoin nodes use the block chain to distinguish legitimate Bitcoin transactions from attempts to re-spend coins that have already been spent elsewhere.
Cryptographic hashes are created from data using an algorithm called SHA-256. Each block contains a number of these hashes; the more hashes in a block, the stronger the chain. This makes it difficult to change a block without redoing the work of finding and calculating the new hash.
Bitcoin nodes use the block chain to distinguish legitimate Bitcoin transactions from attempts to re-spend coins that have already been spent elsewhere.
Bitcoin nodes use the block chain to distinguish legitimate Bitcoin transactions from attempts to re-spend coins that have already been spent elsewhere. The block chain is constantly growing as "completed" blocks are added to it with a new set of recordings.
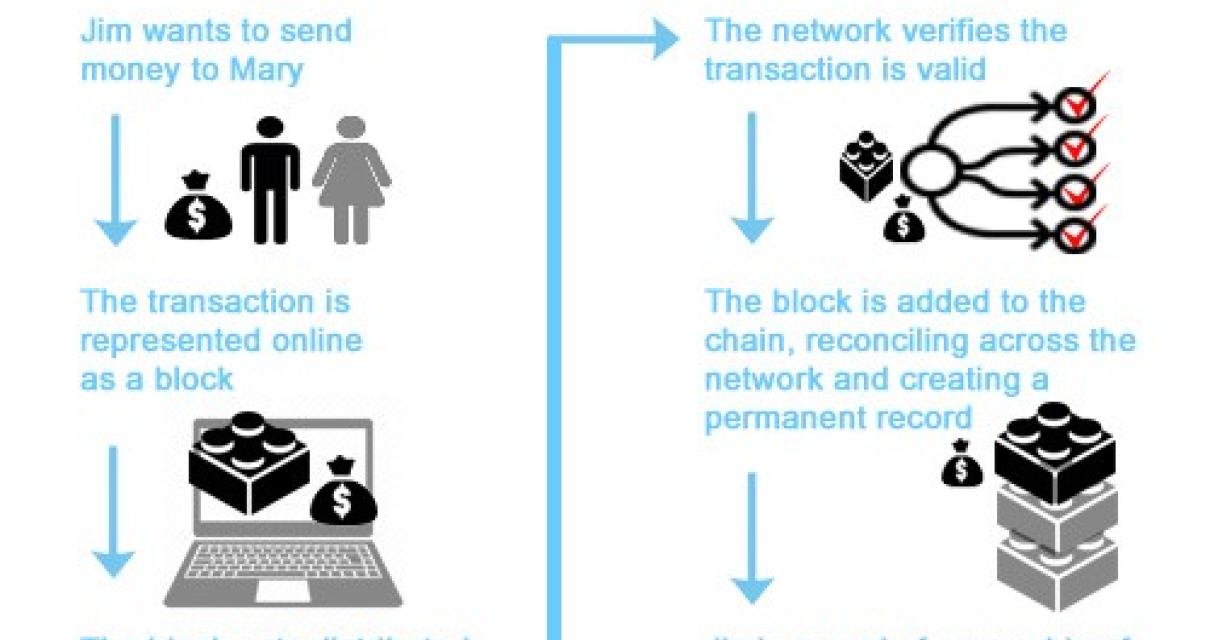
How Does Blockchain Work?
A blockchain is a digital ledger of all cryptocurrency transactions. It is constantly growing as “completed” blocks are added to it with a new set of recordings. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. Bitcoin nodes use the block chain to differentiate legitimate Bitcoin transactions from attempts to re-spend coins that have already been spent elsewhere. Bitcoin nodes use the block chain to distinguish legitimate Bitcoin transactions from attempts to re-spend coins that have already been spent elsewhere.
The Blockchain Explained
The blockchain is a distributed ledger that can record transactions between two parties efficiently and in a verifiable and permanent way. Transactions are grouped into blocks, which are then linked together in a chain. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. Bitcoin, the first and most well-known example of a cryptocurrency, uses a blockchain.
The blockchain is decentralized, meaning it does not rely on any single entity to operate it. Instead, it is maintained by a network of computers spread across the globe. This makes it immune to the whims of governments or financial institutions. The blockchain is also transparent, meaning everyone can see how many blocks are in the chain and what transactions are included in each block.
The benefits of the blockchain are numerous. Transactions are processed quickly and reliably, which reduces the amount of time that is needed to complete a transaction. This allows for more transactions to be processed per second than would be possible using traditional methods. The blockchain also eliminates the need for third-party intermediaries, such as banks.
The downside of the blockchain is that it is not immune to cyberattacks. If someone were to hack into one of the computers that maintains the blockchain, they could potentially alter or delete the records of transactions. Additionally, the blockchain is not reversible, meaning once a transaction has been recorded it is difficult to alter it.
What Is a Blockchain and Why Is It So Important?
A blockchain is a digital ledger of all cryptocurrency transactions. It is essentially a continuously growing list of records, called blocks, that are connected and secured using cryptography. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. Bitcoin, the first and most well-known blockchain, was created in 2009 by an anonymous person or group of people under the name Satoshi Nakamoto.
The blockchain is important because it allows for secure and tamper-proof transactions between two or more parties. It also allows for new forms of transactions that were not possible before, such as peer-to-peer transactions and smart contracts.
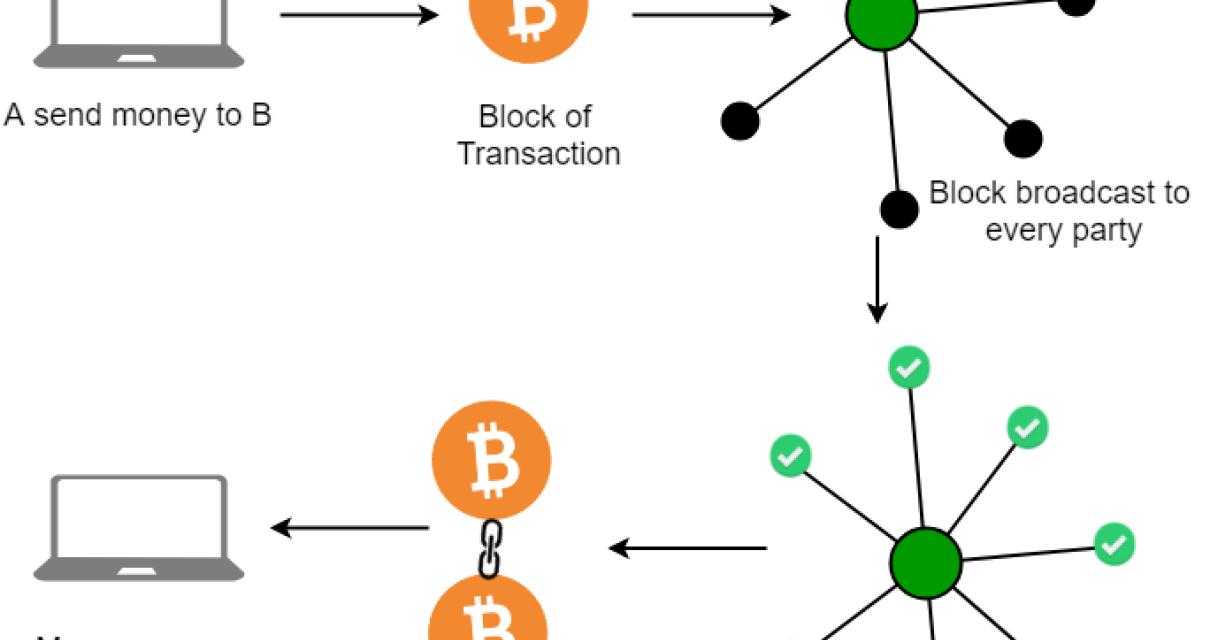
A (Very) Short Introduction to Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is a distributed ledger that allows for secure, transparent and tamper-proof transactions between parties. It operates on a peer-to-peer network and is managed by a network of computers. Transactions are verified by network nodes and recorded in a public registry.
The blockchain technology was first developed in 2009 by an anonymous person or group of people under the name Satoshi Nakamoto. The concept was first presented in a paper titled “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System”. Bitcoin was released as open-source software in 2009.
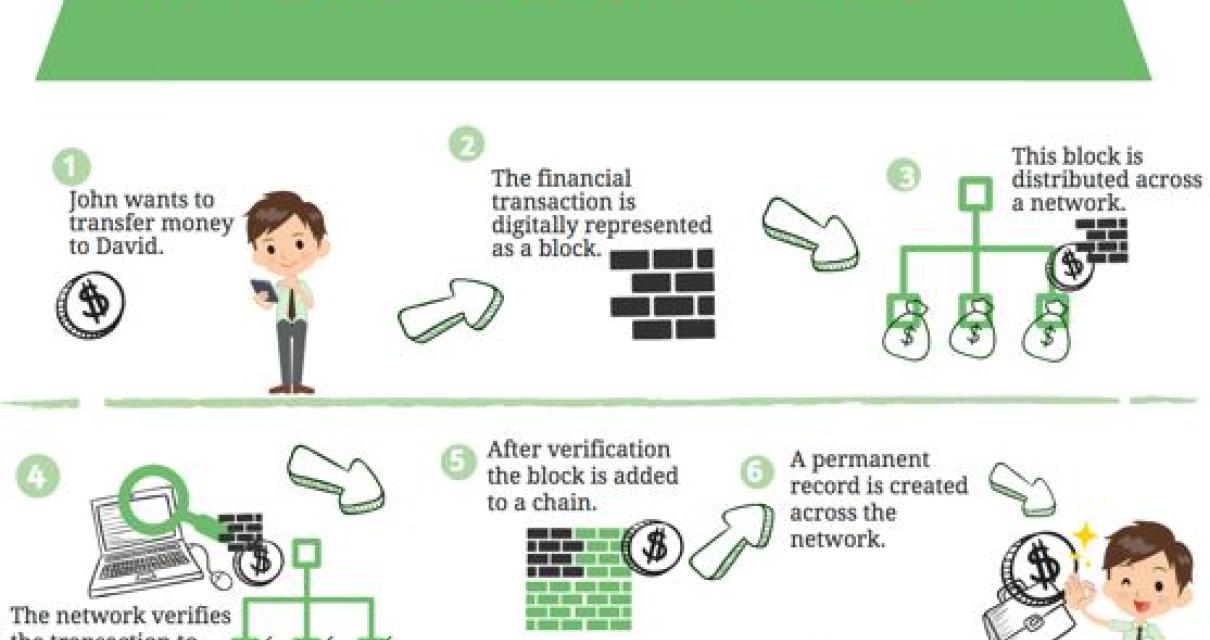
So What Actually is Blockchain?
Blockchain technology is a distributed database that allows for secure, transparent and tamper-proof transactions. Transactions are grouped into blocks and recorded in a chronological order. Each block contains a timestamp, a hash of the previous block, a transaction list and a reward for mining.
The blockchain is constantly growing as “completed” blocks are added to it with a new set of transactions. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the block before it. Bitcoin nodes use the hash of each block to distinguish legitimate Bitcoin transactions from attempts to re-spend coins that have already been spent elsewhere.
An Introduction to Blockchain
Blockchain technology is a distributed database that allows for secure, transparent and tamper-proof transactions. Transactions are verified by network nodes through cryptography and recorded into a public record called a blockchain. Nodes can leave and rejoin the network at will.
The invention of blockchain technology was first proposed by an anonymous person or group of people under the name Satoshi Nakamoto in 2008. Nakamoto designed blockchain to serve as a digital ledger of transactions that could not be changed or falsified by anyone. Transactions are grouped into blocks and then chained together using cryptographic links. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp and transaction data.
Because blockchain is decentralized, it is immune to the threats posed by third-party intermediaries. For example, a bank can’t freeze your assets or arbitrarily change your credit score if you don’t have a traditional bank account. Additionally, blockchain is transparent, meaning everyone can see the transactions taking place. This transparency makes it difficult for criminals to hide their identities or conduct illicit activities.
Although blockchain technology has many benefits, there are also some limitations. For example, blockchain is not able to handle large amounts of data or transactions. Additionally, the technology is still in its early stages and there are some kinks that need to be worked out. However, given the potential benefits of blockchain, developers are working diligently to address these limitations.
blockchain 101: Introduction to blockchain technology
A blockchain is a digital ledger of all cryptocurrency transactions. It is constantly growing as “completed” blocks are added to it with a new set of recordings. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. Bitcoin nodes use the block chain to distinguish legitimate Bitcoin transactions from attempts to re-spend coins that have already been spent elsewhere.
Blockchains are unique in that they allow two parties to transact without the need for a trusted third party. This eliminates the need for financial institutions and other middlemen, which can often add costs and delays to transactions. In addition, blockchain technology provides an immutable record of all transactions, eliminating the risk of fraud or other problems.
Beyond Bitcoin, other cryptocurrencies have begun to use blockchain technology. Ethereum, for example, is a platform on which developers can build applications that run exactly as programmed without any chance of fraud or third-party interference.
What is a cryptocurrency?
A cryptocurrency is a digital or virtual currency that uses cryptography to secure its transactions and to control the creation of new units. Cryptocurrencies are decentralized, meaning they are not subject to government or financial institution regulation. Bitcoin, the first and most well-known cryptocurrency, was created in 2009.
Introducing Blockchain: A Beginner's Guide
What is blockchain?
Bitcoin, Ethereum, and many other blockchain-based cryptocurrencies are based on the technology of blockchain. Blockchain is a distributed database that helps to create an immutable record of transactions. The database is constantly growing as “completed” blocks are added to it with a new set of recordings. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. Bitcoin nodes use the block chain to distinguish legitimate Bitcoin transactions from attempts to re-spend coins that have already been spent elsewhere.
How is blockchain used?
There are many potential applications for blockchain technology, but its most prominent use today is as the underpinning for cryptocurrencies like bitcoin and Ethereum. These platforms allow for peer-to-peer transactions without the need for a third party like a bank or payment processor. Other potential applications for blockchain technology include property ownership registries, supply chains, and digital voting.
Why is blockchain important?
There are several reasons why blockchain is important. First, it is a more secure way to store information than traditional databases. Second, it allows for transparency and trust between parties without the need for a middleman. Third, it is an efficient way to process transactions. Finally, it has the potential to revolutionize how we interact with the digital world.