What is a layer 2 blockchain?
Layer 2 blockchains are a type of blockchain that use a peer-to-peer network to facilitate communication and maintain a record of transactions. This makes layer 2 blockchains more scalable and efficient than other types of blockchains.
What are the benefits of a layer 2 blockchain?
A layer 2 blockchain is a blockchain that operates on a lower level than the traditional blockchain. This means that the layer 2 blockchain can handle more transactions per second than a traditional blockchain. Additionally, a layer 2 blockchain does not require a trustful third party to operate. This makes it an ideal platform for applications that require low latency and high throughput.
What is the difference between a layer 1 and layer 2 blockchain?
Layer 1 blockchain technology is designed to secure and verify transactions without a central authority. It is similar to the way the internet works, with each node participating in a distributed network. Transactions are verified by network participants and recorded in a public ledger.
Layer 2 blockchain technology provides a secure platform for businesses to conduct transactions. Transactions are verified and recorded by nodes in the network, similar to how the internet works. However, layer 2 blockchain technology can also include features that allow it to operate as a decentralized platform.
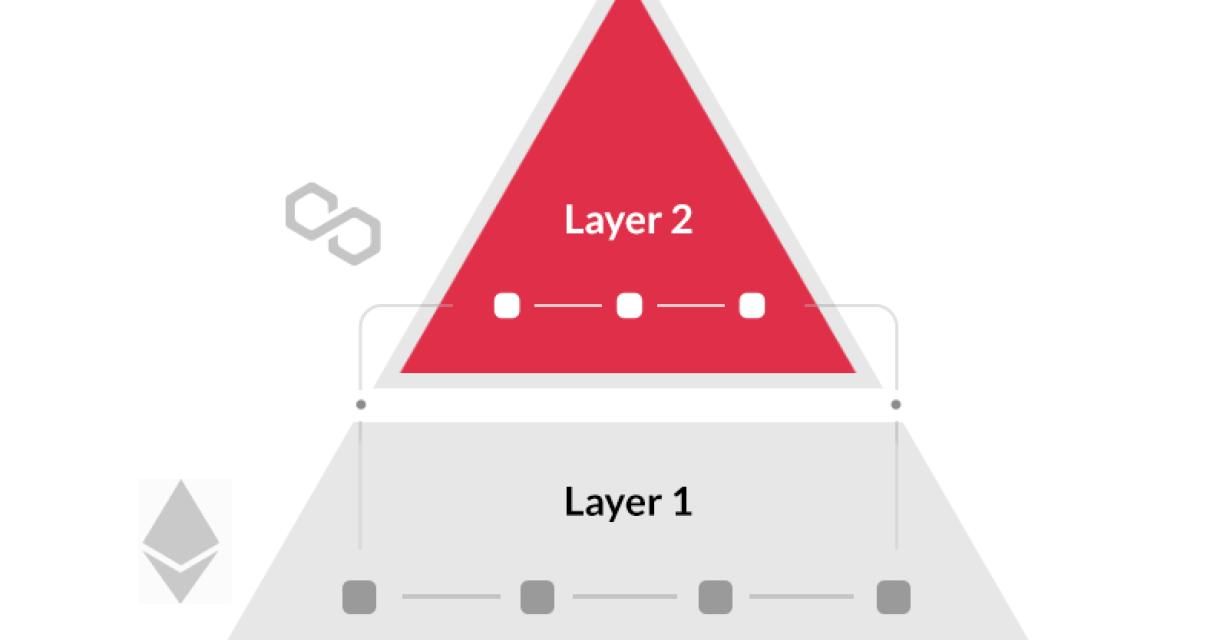
How does a layer 2 blockchain work?
A layer 2 blockchain is a blockchain that operates on a peer-to-peer basis and uses a distributed ledger technology to record transactions. The most common implementation of a layer 2 blockchain is a distributed ledger that uses a shared database to track the ownership of digital assets. This allows multiple parties to participate in the transaction process without having to trust each other.
What are some popular layer 2 blockchains?
Some popular layer 2 blockchains are Ethereum, Bitcoin, Ripple, and Litecoin.
What challenges does a layer 2 blockchain face?
Layer 2 blockchain networks have the potential to enable a more secure and efficient sharing of data across multiple organizations. However, they may face challenges in scalability and adoption due to the need for a larger network of participating nodes.

Why is a layer 2 blockchain needed?
A layer 2 blockchain is needed because it allows for more efficient and secure transfer of data between nodes. A traditional blockchain is a single chain of information that is spread out across a network of nodes. This makes it difficult to verify and tamper with the data. A layer 2 blockchain, on the other hand, creates multiple chains of information that are interconnected but remain separate. This makes it easier to verify and tamper with the data.
What use cases are there for a layer 2 blockchain?
There are many potential use cases for a layer 2 blockchain. Some examples include tracking the provenance of goods, managing digital identities, and providing a tamper-proof record of transactions.
How can a layer 2 blockchain be used to scale Bitcoin?
A layer 2 blockchain can be used to scale Bitcoin by allowing more transactions to be processed at once. This is done by using a different set of rules for how transactions are processed on the layer 2 blockchain than on the main Bitcoin blockchain.
What are some potential problems with a layer 2 blockchain?
Some potential problems with a layer 2 blockchain include:
1. Limited scalability – A layer 2 blockchain can only support a limited number of transactions per second.
2. Inability to verify transactions – A layer 2 blockchain is unable to verify the authenticity of transactions, meaning that it is susceptible to fraud.
3. Lack of security – A layer 2 blockchain is not as secure as a layer 1 blockchain, meaning that it is more likely to be compromised.
What happens if a layer 2 blockchain fails?
If a layer 2 blockchain fails, the nodes on the network will be unable to communicate with each other. This can result in a loss of funds and/or an inability to process transactions.