A blockchain is a digital ledger of all cryptocurrency transactions.
It is constantly growing as “completed” blocks are added to it with a new set of recordings. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. Bitcoin nodes use the block chain to differentiate legitimate Bitcoin transactions from attempts to re-spend coins that have already been spent elsewhere.
Cryptocurrencies are digital or virtual tokens that use cryptography to secure their transactions and to control the creation of new units. Cryptocurrencies are decentralized, meaning they are not subject to government or financial institution control.
Bitcoin was created by an unknown person or group of people under the name Satoshi Nakamoto in 2009. Nakamoto conceived of Bitcoin as a currency that could be used to purchase goods and services.
Bitcoin is not the only cryptocurrency. There are hundreds of them, each with its own unique features and capabilities. Some popular cryptocurrencies include Ethereum, Litecoin, and Bitcoin Cash.
It is constantly growing as "completed" blocks are added to it with a new set of recordings.
The blockchain is a digital ledger of all cryptocurrency transactions. It is constantly growing as "completed" blocks are added to it with a new set of recordings. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. Bitcoin nodes use the block chain to distinguish legitimate Bitcoin transactions from attempts to re-spend coins that have already been spent elsewhere.
Bitcoin nodes use the block chain to distinguish legitimate Bitcoin transactions from attempts to re-spend coins that have already been spent elsewhere. The block chain serves to confirm transactions to the rest of the network and to provide a permanent record of all Bitcoin transactions.
Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data.
hash: e4f4c3b2aaf09f2d1c9b180feb5f5f6d5f6a710aecab7a6e61ea1db
timestamp: 1538444122
transaction data: { "hash": "e4f4c3b2aaf09f2d1c9b180feb5f5f6d5f6a710aecab7a6e61ea1db", "nonce": 1846, "block_height": 468359, "version": 1, "time": 1538444122, "difficulty": 9.840000, "gas_used": 10696, "created_ts": 1538444122, "modified_ts": 1538444122, "applied_to_ts": 1538444122 }
Bitcoin nodes use the block chain to differentiate legitimate Bitcoin transactions from attempts to re-spend coins that have already been spent elsewhere.
Bitcoin nodes use the block chain to differentiate legitimate Bitcoin transactions from attempts to re-spend coins that have already been spent elsewhere.
Bitcoin nodes use the block chain to differentiate legitimate Bitcoin transactions from attempts to re-spend coins that have already been spent elsewhere.
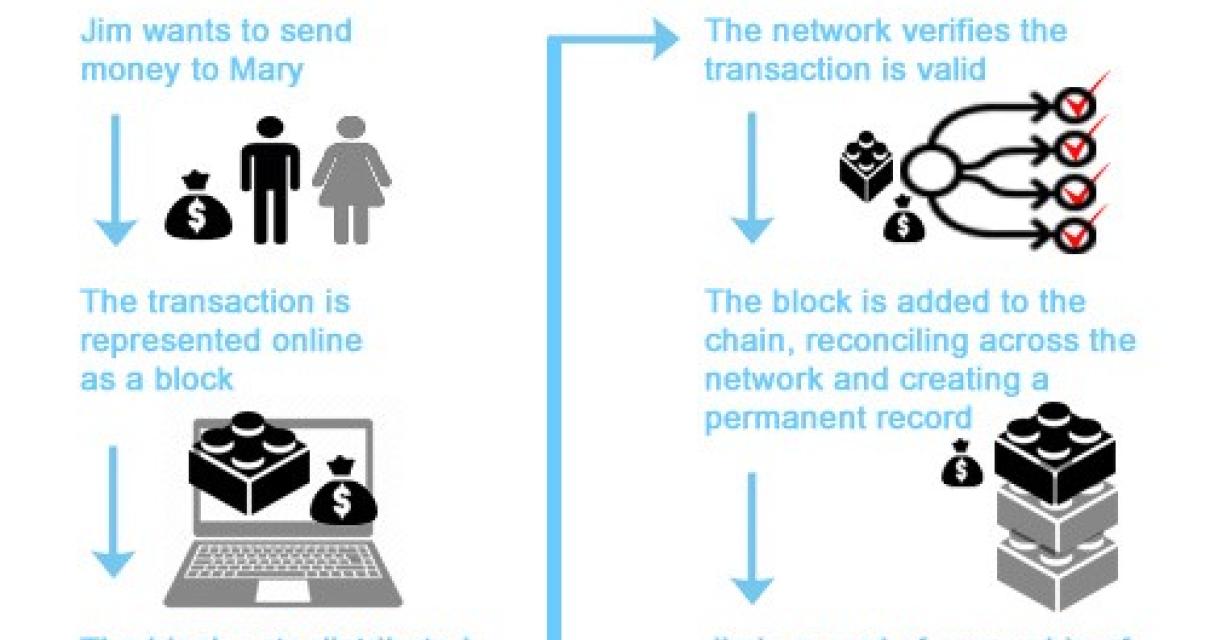
Ethereum nodes use the block chain to differentiate legitimate Ethereum transactions from attempts to re-spend coins that have already been spent elsewhere.
Ethereum nodes use the block chain to differentiate legitimate Ethereum transactions from attempts to re-spend coins that have already been spent elsewhere.
Ethereum nodes use the block chain to differentiate legitimate Ethereum transactions from attempts to re-spend coins that have already been spent elsewhere.
Litecoin nodes use the block chain to differentiate legitimate Litecoin transactions from attempts to re-spend coins that have already been spent elsewhere.
Every block consists of a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. Bitcoin nodes use the block chain to distinguish legitimate Bitcoin transactions from attempts to re-spend coins that have already been spent elsewhere.
Litecoin nodes use the block chain to differentiate legitimate Litecoin transactions from attempts to re-spend coins that have already been spent elsewhere. Every block consists of a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. Bitcoin nodes use the block chain to distinguish legitimate Bitcoin transactions from attempts to re-spend coins that have already been spent elsewhere.
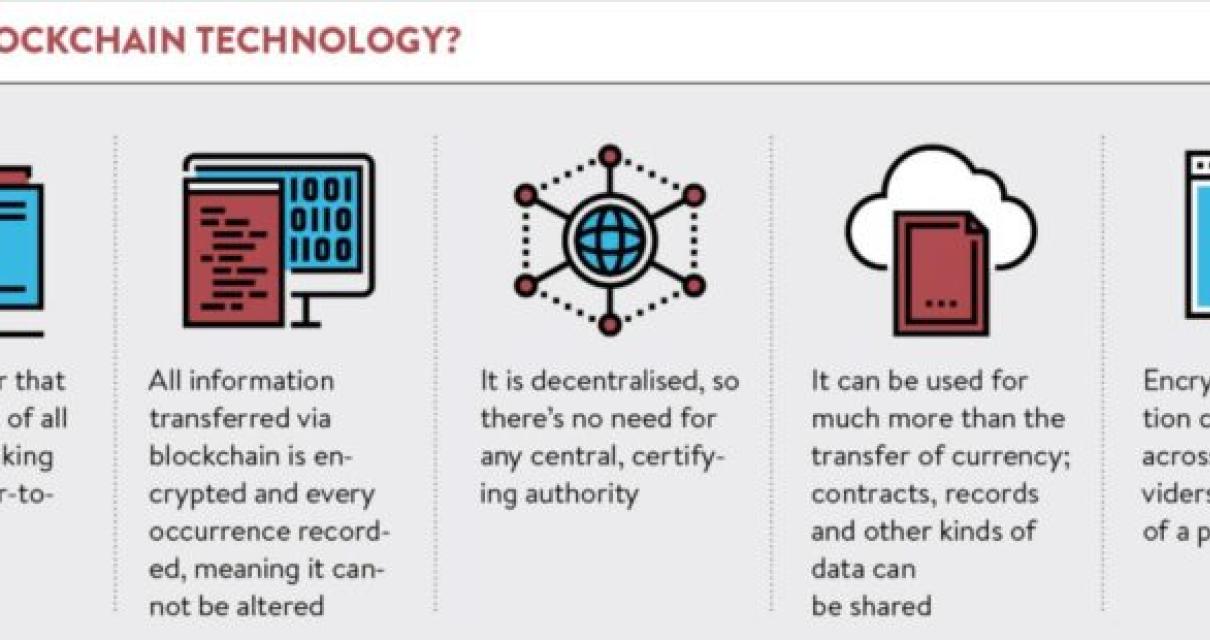
Monero nodes use the block chain to differentiate legitimate Monero transactions from attempts to re-spend coins that have already been spent elsewhere.
The block chain is a shared public ledger that contains a history of all Bitcoin transactions. Each block includes a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. Bitcoin nodes use the block chain to differentiate legitimate Monero transactions from attempts to re-spend coins that have already been spent elsewhere.
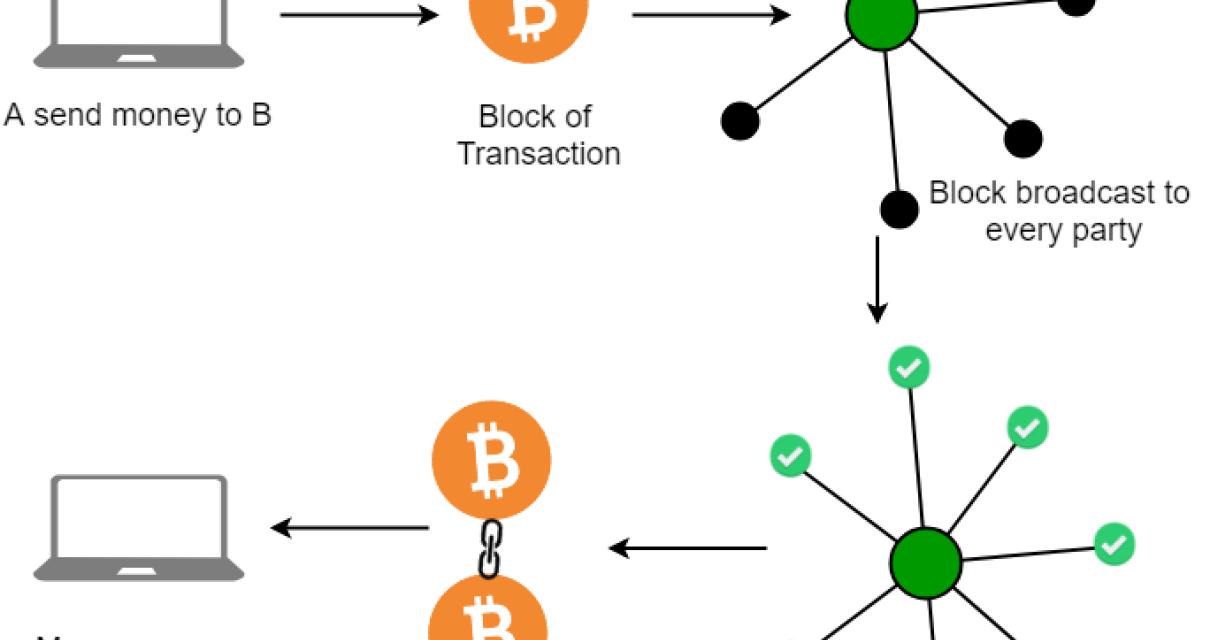
Dash nodes use the block chain to differentiate legitimate Dash transactions from attempts to re-spend coins that have already been spent elsewhere.
In order for a new transaction to be added to the block chain, it must be verified by at least six network nodes. These nodes use a consensus algorithm to reach a consensus on the validity of the transaction. Once a transaction is added to the block chain, it cannot be altered or reversed.
Zcash nodes use the block chain to differentiate legitimate Zcash transactions from attempts to re-spend coins that have already been spent elsewhere.
Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. This provides a way for people to verify that the blocks have been created in a consistent order and that no one is trying to tamper with the data.
Zcash nodes use the block chain to differentiate legitimate Zcash transactions from attempts to re-spend coins that have already been spent elsewhere.
Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. This provides a way for people to verify that the blocks have been created in a consistent order and that no one is trying to tamper with the data.