What is a Blockchain?
A blockchain is a digital ledger of all cryptocurrency transactions. It is constantly growing as "completed" blocks are added to it with a new set of recordings. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. Bitcoin nodes use the block chain to differentiate legitimate Bitcoin transactions from attempts to re-spend coins that have already been spent elsewhere.
What is a Blockchain and how does it work?
A blockchain is a distributed database that allows for secure, transparent and tamper-proof transactions. It is essentially a digital ledger of all cryptocurrency transactions. Transactions are grouped into blocks and then linked together with cryptographic chains. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp and transaction data. Transactions are verified by network nodes and then added to the blockchain. Once a block is added, it is difficult to change or remove. This makes it an effective way to monitor and track cryptocurrency transactions.
What is a Blockchain? How does it work?
A blockchain is a distributed database that allows for secure, transparent and tamper-proof tracking of assets. Transactions are recorded in a chronological order and are verified by network nodes. Bitcoin, Ethereum and other cryptocurrencies use blockchains.
The Basics of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is a distributed database that uses a secure cryptographic algorithm to record transactions between parties. The ledger is transparent and tamper-proof and can be used to track the ownership of assets. Transactions are verified by network nodes through cryptography and recorded in a public distributed ledger.
The key benefit of blockchain technology is that it allows for secure, tamper-proof and transparent transactions that can be tracked and verified. This makes it an attractive solution for a wide range of applications, including financial services, supply chains and online transactions.
How Does Blockchain Work?
Blockchain technology operates on a distributed ledger, or database, which is stored on a network of computers. Each node on the network stores a copy of the ledger and participates in verifying and recording transactions.
Each block in the blockchain contains a hash of the previous block, a timestamp and transaction data. Nodes use the hash function to verify the authenticity of each block, preventing tampering. Once a block is verified, it is added to the blockchain and the associated timestamp is updated.
Blocks are added to the blockchain in chronological order, which makes it difficult to tamper with the ledger. Because blocks are added to the blockchain in chronological order, tampering with one block would not cause the rest of the blockchain to be invalidated. However, tampering with a block that is later in the blockchain would cause the entire blockchain to be invalidated.
How Does Blockchain Work with Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is the first and most well-known application of blockchain technology. Bitcoin works as a digital currency that is created, transferred and verified through blockchain technology.
Users can purchase bitcoin through a digital currency exchange and then use it to purchase goods and services. Bitcoin is also used to pay for goods and services with other digital currencies, such as Ethereum.
Bitcoin works as a digital currency because it is decentralized. There is no central authority that controls or manages bitcoin. Instead, bitcoin is managed by a network of computers that are responsible for verifying and recording transactions.
How Does Blockchain Work with Ethereum?
Ethereum is another application of blockchain technology that works as a decentralized platform for developing smart contracts and applications. Ethereum works similar to bitcoin in that it is used as a digital currency and payment system.
However, Ethereum also allows for smart contracts and applications to be built on its platform. Smart contracts are computer codes that are automatically executed when certain conditions are met. This allows for a variety of applications to be built on Ethereum, such as financial contracts, healthcare records and supply chains.
What Are the Key Advantages of Blockchain Technology?
The key advantages of blockchain technology include:
Secure: Blockchain technology uses a secure cryptographic algorithm to record transactions between parties. This ensures that transactions are tamper-proof and secure.
Transparent: The ledger is transparent and can be used to track the ownership of assets. This makes it an attractive solution for a wide range of applications, including financial services, supply chains and online transactions.
Tamper-proof: Nodes use the hash function to verify the authenticity of each block, preventing tampering. This prevents unauthorized changes to the ledger and protects against fraud.
Verifiable: The blockchain is decentralized and can be used to track the ownership of assets. This makes it an accurate and reliable solution for tracking assets.
What Are the Disadvantages of Blockchain Technology?
The key disadvantages of blockchain technology include:
Inability to scale: Blockchain technology is not able to handle large volumes of transactions. This limits its potential applicability in financial services, supply chains and online transactions.
Cost: Blockchain technology is expensive to implement and maintain. This limits its potential applicability in mainstream applications.
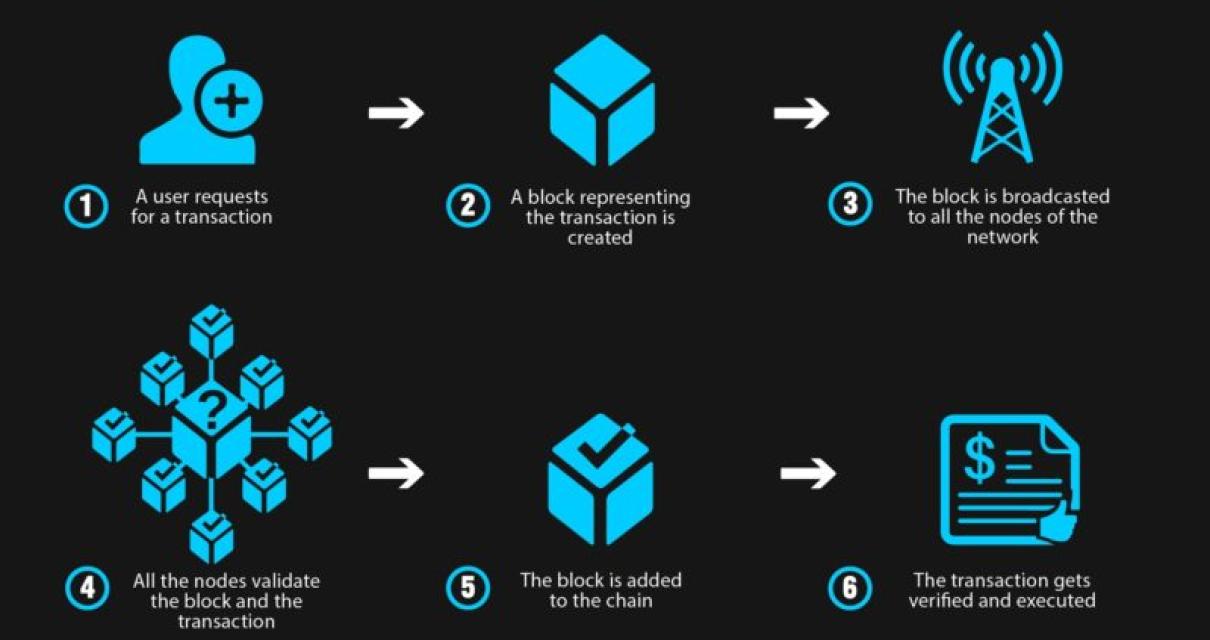
How Does a Blockchain Work?
A blockchain is a distributed database that allows for secure, tamper-proof transactions. Transactions are grouped into blocks, which are linked together with cryptographic chains. Each block contains a timestamp, a hash of the previous block, and transaction data. The blockchain is constantly growing as new blocks are added.
Each node in the network has a copy of the blockchain. When a node wants to make a new transaction, it checks to see if the transaction is already in the blockchain. If it is, the node can simply update the data in the block and send the updated block to other nodes. If the transaction is not in the blockchain, the node creates a new block and adds the transaction data to it.
Once a block is added to the blockchain, it is difficult to change. Any node that tries to change the block will get an error message. This ensures that the blockchain is tamper-proof.
The Blockchain Explained
The blockchain is a digital ledger of all cryptocurrency transactions. It is constantly growing as "completed" blocks are added to it with a new set of recordings. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. Bitcoin nodes use the block chain to differentiate legitimate Bitcoin transactions from attempts to re-spend coins that have already been spent elsewhere.
Bitcoin was the first successful implementation of blockchain technology, and the genesis block of the blockchain is still located here: https://blockchain.info/blocks/000000000019d3b4.

Introducing the Blockchain
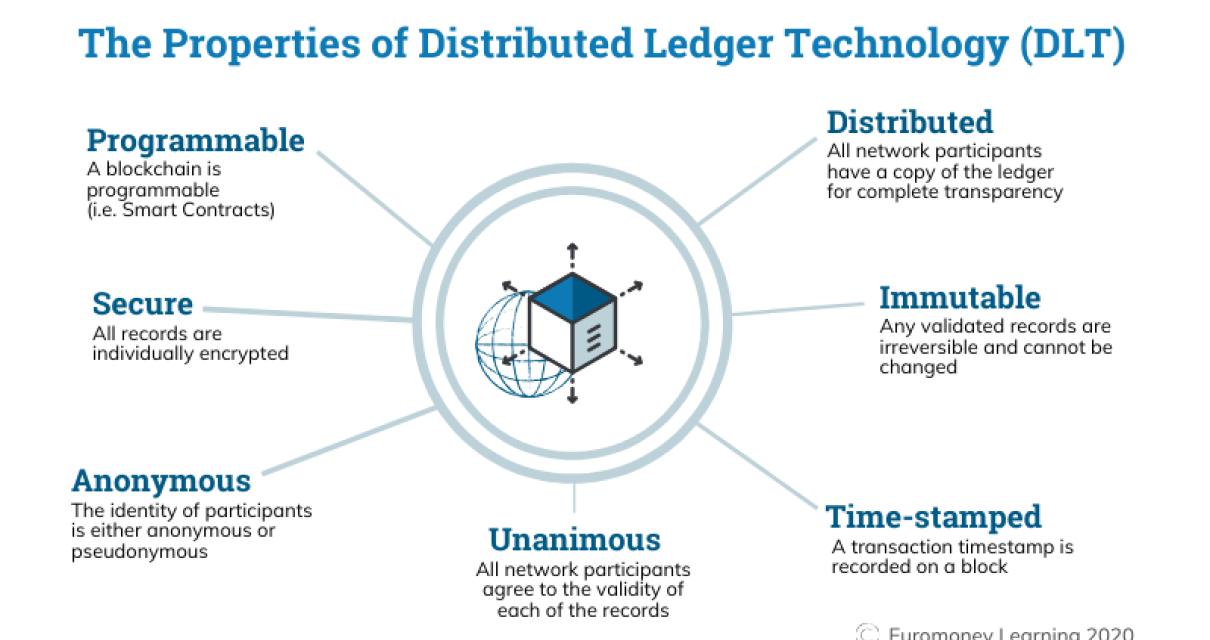
A blockchain is a distributed database that allows for secure, transparent, and tamper-proof transactions. Its users can maintain an up-to-date copy of the blockchain ledger without need for central authorities.
A blockchain is decentralized and therefore not subject to government interference or control. This makes it ideal for use in a variety of industries, including financial services, healthcare, and supply chains.
How Does the Blockchain Work?
A blockchain database is continuously growing as “completed” blocks are added to it with a new set of recordings. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. To modify a block, an attacker would need to solve a complex mathematical problem first. Bitcoin, for example, uses Hashcash puzzles to prevent such attacks.
Transactions are verified by network nodes through cryptography and recorded in a public distributed ledger called a blockchain. Bitcoin nodes use the block chain to differentiate legitimate Bitcoin transactions from attempts to re-spend coins that have already been spent elsewhere.
The blockchain is constantly growing as “completed” blocks are added to it with a new set of recordings.
How the Blockchain Works
The blockchain is a distributed database that maintains a continuously growing list of records called blocks. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. Bitcoin miners use their computers to solve complex mathematical problems to create new blocks. Once a miner creates a new block, they broadcast it to the network and receive a reward in bitcoin. This process is called mining.
Every time a user makes a transaction, the blockchain updates the record of that transaction in a manner that is verified by the network. This verification process is how the blockchain ensures that every transaction is legitimate. Bitcoin nodes use the block chain to distinguish legitimate Bitcoin transactions from attempts to re-spend coins that have already been spent elsewhere.
Understanding the Blockchain
The blockchain is a digital ledger of all cryptocurrency transactions. It is constantly growing as "completed" blocks are added to it with a new set of recordings. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp and transaction data. Bitcoin nodes use the block chain to distinguish legitimate Bitcoin transactions from attempts to re-spend coins that have already been spent elsewhere.
The blockchain is constantly growing as "completed" blocks are added to it with a new set of recordings.
What is a Blockchain?
A blockchain is a digital ledger of all cryptocurrency transactions. It is constantly growing as "completed" blocks are added to it with a new set of recordings. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. Bitcoin nodes use the block chain to distinguish legitimate Bitcoin transactions from attempts to re-spend coins that have already been spent elsewhere.